* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Sympathetic and Parasympathetic
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Electromyography wikipedia , lookup
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
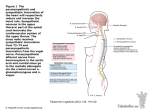
Sympathetic and parasympathetic nerves Nervous system The nerves system composed of all nerve tissue in the body The function of nerves tissue are to receive stimuli, transmit and initiate response Autonomic nervous system Mostly motor nerves controls function of involuntary and smooth muscles eg. cardiac muscles The autonomic nervous system provides almost every organ with and double set of nerves. Sympathetic parasympathetic Autonomous nervous system The nervous system controls the functions of the body which are carried out automatically, Rate and force of the heart beat Secretion of the glands Vasoconstriction or vasodilation Change in the size of the pupils of the eye Sympathetic and parasympathetic nerves Sympathetic Activates and prepares the body for vigorous muscular activity stress and emergencies Parasympathetic Lower activity, operates during normal situations, permits digestion and conservation of energy. Sympathetic & parasympathetic Muscle Origin Action innervation pupillae, dilator Inner margin of iris dilates pupil Sympatheti c fibers via short ciliary nerves, synapsing in superior cervical sympathetic ganglion pupillae, Encircles iris Constricts the pupil parasympath etic fibers of oculomotor nerve (III), synapsing in ciliary ganglion sphincter Sympathetic nerve Nerve Source Branches Motor oculomotor oculomotor nuclei of midbrain (pre ganglionic parasympath superior br., inferior br. etic) ciliary muscle & sphincter pupillae (GVE preganglioni c parasympat hetic to ciliary ganglion via parasympat hetic root, Sensory Notes ----------- also known as: CN III, 3rd cranial nerve; passes through superior orbital fissure Nerve Source zygomatic Maxillary Division of Trige minal(V2 Branches Motor Sensory zygomatico secretomotor skin of facial & (postgang. Face zygomatico parasymp.) lateral & temporal to lacrimal Superior gland (via to orbit fibers from pterygopalat ine gang. that reach lacrimal n. by communicat ing br. of zygomaticot emporal) Notes carries postganglionic parasympatheti c axons to the lacrimal gland that have synapsed in the pterygopalatine ganglion Autonomic drugs Autonomic drugs acts on spincter and dilator pupillae muscles of the iris and also on the ciliary muscles Miotics Mydriatics - pupil constricting pupil dilating Parasympathetic mydriatics The abolish the action of acetylcboline and thus cause mydriatics by making It impossible for the sphincter muscles to contract (eg. Atropine1%, homatropine 1-2%, hyosine (0.11%, cyclopentolate 0.5% - 1 and tropicamide 0.5-1%) Sympathetic mydriatics Directly act on dilation pupillae to produce mydriatics (eg. Adrenaline as is tra-cameral injection, Phenylpherine drops 2.5-10%) and locaine hydrocholoride)