* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 9. Cardio Control
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Aortic stenosis wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
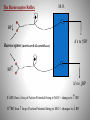
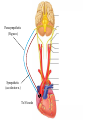
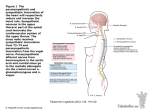
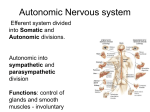
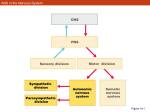
The Baroreceptor Reflex Sensory Receptors Detect Changes in BP Specifically - Mechanoreceptors detect changes in BP Located in blood vessel walls: 1. Aortic bodies 2. Carotid bodies The Baroreceptor Reflex M.O. BP↓ Baroreceptors (aortic arch & carotid a.a.) ∆’s to ↑BP BP↑ ∆’s to ↓BP If BP, then freq of Action Potential firing to M.O > changes to BP. If BP, then freq of Action Potential firing to M.O > changes to BP. Modulation of the Heart by the ANS At rest, heart has Parasympathetic modulation (slows it from 90-100 down to 70-80 beats/min). When excited, Para dissipates and Sym takes over. When heart has Sympathetic modulation (increases to ~120 beats/min). Parasympathetic (Vagus n.) Sympathetic (accelerator n.) To SA node The Medulla Oblongata the ANS and the Cardiovascular System Parasympathetic Stimulation Lowers BP Sympathetic Stimulation Elevates BP Modulation of the Heart the Endocrine System Hormones, such as E stimulate the heart rate and force of contraction (S.V.) via receptors. Atrial Natriuretic Peptide (ANP) is released from the atria when the heart is over-stretched. ANP Causes: 1) vasodilation and 2) Na+ excretion