* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 6 Tour of the Cell II
Survey
Document related concepts
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
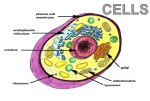
A Tour of the Cell, Part II CHAPTER 4 Features of the Eukaryotic Cell, cont. Endomembrane System, continued o Golgi Apparatus o Lysosomes o Vacuoles Energy Converting Organelles o Chloroplasts o Mitochondria Cytoskeleton o Cell Shape o Cell Movement Proteins and Lipids Leave the ER Enroute to the Golgi Proteins Are Transported in Vesicles to the Golgi Figure 4.11 The Golgi Apparatus • The Golgi apparatus – Refines, stores, and distributes the chemical products of cells. – Acts like a finishing and shipping station (UPS or FedEx) in the cell A Tour of the Cell, Part II CHAPTER 4 Features of the Eukaryotic Cell, cont. Endomembrane System, continued o Golgi Apparatus o Lysosomes o Vacuoles Energy Converting Organelles o Chloroplasts o Mitochondria Cytoskeleton o Cell Shape o Cell Movement Lysosomes • A lysosome is a membrane-enclosed sac containing digestive enzymes – The enzymes break down macromolecules and ingested debris within vacuoles – Serves as the “Greeting and Garbage Service” of the cell Lysosome Formation Figure 4.13a A Tour of the Cell, Part II CHAPTER 4 Features of the Eukaryotic Cell, cont. Endomembrane System, continued o Golgi Apparatus o Lysosomes o Vacuoles Energy Converting Organelles o Chloroplasts o Mitochondria Cytoskeleton o Cell Shape o Cell Movement Vacuoles • Vacuoles are membranous sacs. – Two types are the contractile vacuoles of protists and the central vacuoles of plants. – Used to store food, water, or wastes Paramecium vacuole Flow of Proteins Through the Endomembrane System Figure 4.15 A Tour of the Cell, Part II CHAPTER 4 Features of the Eukaryotic Cell, cont. Endomembrane System, continued o Golgi Apparatus o Lysosomes o Vacuoles Energy Converting Organelles o Chloroplasts o Mitochondria Cytoskeleton o Cell Shape o Cell Movement Energy Conversion Organelles: Chloroplasts and Mitochondria Copyright © 2007 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings Chloroplasts • Chloroplasts are the sites of photosynthesis, the conversion of light energy to chemical food energy – They are food production factories and are found only in plants and some protists (algae & seaweed) Photosynthesis: Carbon dioxide + water + sunlight Food energy + oxygen gas Mitochondria • Mitochondria are energy conversion factories • Food energy is converted into usable cellular energy (ATP) through cellular respiration Cell Respiration: Food energy + oxygen gas Carbon dioxide + water + ATP Unusual Features of Mitochondria and Chloroplasts • Mitochondria and chloroplasts share another feature unique among eukaryotic organelles. – They contain their own DNA.in the form of small, circular loops. • The existence of separate “mini-genomes” is believed to be evidence that – Mitochondria and chloroplasts evolved from free-living prokaryotes in the distant past. A Tour of the Cell, Part II CHAPTER 4 Features of the Eukaryotic Cell, cont. Endomembrane System, continued o Golgi Apparatus o Lysosomes o Vacuoles Energy Converting Organelles o Chloroplasts o Mitochondria Cytoskeleton o Cell Shape o Cell Movement The Cytoskeleton: Cell Shape and Movement • The cytoskeleton is an infrastructure of the cell consisting of a network of fibers. – Made of microtubules and microfilaments • Functions: – Provide mechanical support, maintain or change its shape – Provide for whole cell movement Cytoskeleton: Cilia and Flagella • Cilia and flagella are hair-like appendages, that provide a means of cellular movement. – Flagella propel the cell in a whiplike motion. – Cilia move in a coordinated back-and-forth motion. Cilia and Flagella Paramecium Cilia Cilia found on anchored cells create currents and streaming in liquids Figure 4.19c A Tour of the Cell CHAPTER 4 Microscopes as Windows on Cells o Types of Microscopes o Magnification and Resolution Categories of Cells Features of Prokaryotic Cells Features of Eukaryotic Cells o Membrane Structure o Nucleus and Ribosomes o Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) o Golgi Apparatus o Lysosomes o Vacuoles o Energy Converting Organelles – Chloroplasts – Mitochondria o Cytoskeleton – Cell Shape – Cell Movement

































![Student_Work_files/how cells keep us alive[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008096061_1-3bccda7a250f4b6d053f03d6cd844694-150x150.png)
