* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Edward Flatau wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience and intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
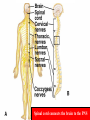
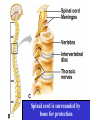
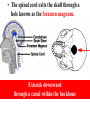
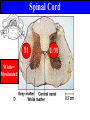
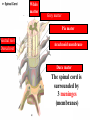
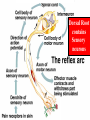
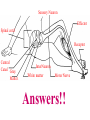
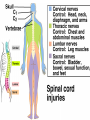
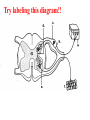
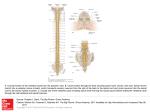
Spinal cord connects the brain to the PNS Spinal cord is surrounded by bone for protection How big is the actual cord? Very small!!! Look for the H!! H is the gray matter • The spinal cord exits the skull through a hole known as the foramen magnum. Extends downward through a canal within the backbone Spinal Cord Contains 2 types of nerve tissue---gray and white matter 1. White matter is myelinated (W/M) – made mostly of interneurons 2. Gray matter is central and unmyelinated – made of cell bodies of motor neurons Spinal Cord M White= Myelinated U/M White matter Grey matter Pia mater Ventral root Dorsal root Arachnoid membrane Dura mater The spinal cord is surrounded by 3 meninges (membranes) Dorsal Ventral Dorsal Root contains Sensory neurons Try labeling this diagram!! Answers on the next slide! Sensory Neuron Effector Spinal cord Receptor Central Canal InterNeuron Gray Matter White matter Motor Nerve Answers!! Different parts of the spinal cord control different parts of the body This info is used a lot by chiropractors & physiotherapists! Try labeling this diagram!!