* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nervous System: Spine
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
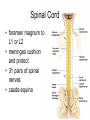
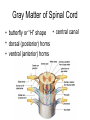
Why have paths cross R to L in the brain? • scientists not sure • possibly due to evolutionary process Chapter 7: The Spinal Cord Spinal Cord • 17 inches long • provides 2-way conduction pathway to and from the brain • major reflex center Spinal Cord • foramen magnum to L1 or L2 • meninges cushion and protect • 31 pairs of spinal nerves • cauda equina Gray Matter of Spinal Cord • central canal • butterfly or “H” shape • dorsal (posterior) horns • ventral (anterior) horns Gray Matter of Spinal Cord • dorsal horn – association neurons • dorsal root – ganglion: cell bodies of sensory neurons • ventral horn – cell bodies of motor neurons • ventral root – axons of motor neurons White Matter of Spinal Cord • what makes it white? • 3 regions or columns – posterior • sensory (afferent) tracts – lateral • motor (efferent) tracts – anterior • motor (efferent) tracts Damage to Spinal Cord • spastic paralysis • quadriplegic vs. paraplegic Lab • Start with sheep brain dissection. – answer questions - pp 120-122 – Review Sheet 14 - pp 295-299 • on human brain model – find internal and external brain structures – trace path of CSF through human brain model – identify cranial nerves • if you do not finish, USE THE OPEN LABS