* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Genetics Review
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
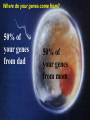
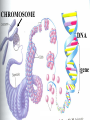
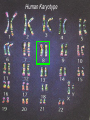
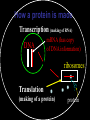
Genetics Review Honors Human Anatomy & Physiology Mr. Mazza 2009-10 Why review genetics in a course on anatomy & physiology? Genes control the layout, make-up and function of the bodies of all organisms. Examples of traits influenced by genes: • Appearance (hair, skin, eyes, height, etc.) • Body structure of an organism • Susceptibility to diseases • Personality traits • Behavior (instincts as well as other behaviors) *Environment interacts with genes to produce the final phenotype (physical trait) Where do your genes come from? 50% of your genes from dad 50% of your genes from mom It’s the stuff that genes are made of: DNA • made of 4 • • nitrogenous bases (adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine) A pairs with T; C pairs with G Each gene is a unique sequence of the 4 bases CHROMOSOME DNA gene What information do genes contain? • Each gene on the DNA is an instruction to build a protein • Proteins are the main structural components of the body (bones, muscle, skin, hair, nails, blood vessels, organs, etc.) and regulate all chemical reactions in the body Human Karyotype From Genes to Proteins How a protein is made Transcription (making of RNA) DNA mRNA (has copy of DNA information) ribosomes Translation (making of a protein) protein The Genetic Code Each protein is made of amino acids - every 3 bases is a codon (code) for one amino acid mutation A change in the genetic code Flow of genetic information in a cell (Central dogma of molecular biology): DNA Mutated DNA RNA Mutated RNA PROTEIN Defective protein Why is this important? • Our susceptibility to any disease is affected by the variations of genes we inherit from our parents and/or mutations we get via the environment (i.e. radiation, chemical exposure, etc.)