* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Human Genome Project - College Heights Secondary School
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
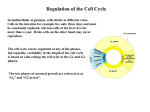
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Metagenomics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Essential gene wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Transposable element wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Pathogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Human Genome Project wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Human Genome Project Animation Overview - Click • What did they do? • Why did they do it? • What will it mean for humankind? Brief history of the work… • Proposed in 1985 • 1988. Initiated and funded by NIH and US Dept. of Energy ($3 billion set aside) • 1990. Work begins. • Published in Science and Nature in February, 2001 Goals of HGP • Create map of the 22 human chromosomes, X / Y) • Identify the entire set of genes & map them all to their chromosomes • Determine the nucleotide sequences of the estimated 3 billion base pairs • Analyze genetic variation among humans Model organisms • • • • • Bacteria (E. coli, influenza, several others) Yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) Plant (Arabidopsis thaliana) Fruit fly (Drosophila melanogaster) Mouse (Mus musculus) Goals of HGP (cont’d) • Develop new laboratory and computing technologies to make all this possible • Disseminate genome information • Consider ethical, legal, and social issues associated with this research How they did it… • DNA from 5 humans • 2 males, 3 females • 2 caucasians, one each of asian, african, hispanic • Cut up DNA with restriction enzymes • Sequenced the fragments • Let a supercomputer put the pieces together Human genome content • • • • 1-2 % codes for protein products 24% important for translation 75% “junk” Repetitive elements – Transposons – Retrotransposons BOOK THAT WROTE ITSELF Comparative Genomics Yeast • 70 human genes are known to repair mutations in yeast •Nearly all we know about cell cycle and cancer comes from studies of yeast •Advantages: •fewer genes (6000) •few introns • 31% of yeast genes give same products as human homologues Drosophila • nearly all we know of how mutations affect gene function come from Drosophila studies •We share 50% of their genes •61% of genes mutated in 289 human diseases are found in fruit flies •68% of genes associated with cancers are found in fruit flies Mouse • known as “mini” humans •Very similar physiological systems •Share 90% of their genes