* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CentralDogmaNotes
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid tertiary structure wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Transfer RNA wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
History of RNA biology wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
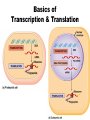
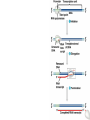
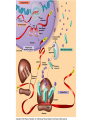
From Gene to Protein Central Dogma The Big Picture • The information content of DNA is in the form of specific sequences of nucleotides • The DNA inherited by an organism leads to specific traits by dictating the synthesis of proteins • Gene expression, the process by which DNA directs protein synthesis, includes two stages: transcription and translation • The ribosome is part of the cellular machinery for translation, polypeptide synthesis Basics of Transcription & Translation The Protein Code • The genetic code is redundant but not ambiguous; no codon specifies more than one amino acid • Codons must be read in the correct reading frame (correct groupings) in order for the specified polypeptide to be produced • The genetic code is nearly universal • Genes can be transplanted, then transcribed & translated Type of RNA Functions Messenger Carries information specifying RNA (mRNA) amino acid sequences of proteins from DNA to ribosomes Transfer RNA Serves as adapter molecule in (tRNA) protein synthesis; translates mRNA codons into amino acids Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) Plays catalytic (ribozyme) roles and structural roles in ribosomes Point Mutation Frameshift Mutation