* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download cell membrane
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
SNARE (protein) wikipedia , lookup
Theories of general anaesthetic action wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Model lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
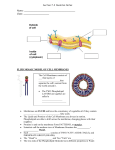
Cellular Transport: Cell Membrane How Molecules Are Transported Across The Cell Membrane. Essential Questions • How do cells maintain homeostasis? • How are cell membranes (plasma membranes) selectively permeable (semi-permeable)? • Why is it important that cells are able to transport molecules with (active transport) and without (passive transport) energy? Cell Membranes • Functions: a. Controls what enters and exits the cell to maintain homeostasis b. Provides protection and support for the cell TEM picture of a real cell membrane. What is the purpose of cellular transport? • Homeostasis depends upon appropriate movement of materials across the cell membrane. • The cell membrane regulates the passage of materials into and out of the cell. – Needed (required) materials move in • Ex. Oxygen and glucose – Excess materials or wastes move out • Ex. The CO2 produced as waste product of cellular respiration How? • A cell membrane is semi-permeable (selectively permeable) – means some substances can pass directly through cell membrane while other substances can not. • Materials enter or exit through the cell membrane either passive transport or active transport. What is a membrane made of? • Phospholipid – lipid made of a phosphate group and 2 fatty acids. – 1 polar head – phosphate group • Hydrophilic -loves water – 2 non-polar tails fatty acids • Hydrophobic -hates water Draw in Journal • Lipid bilayer – double layer of phospholipids – polar head of one faces outside and other faces inside of cell – Non-polar tails face towards each other inside bilayer Draw in Journal • Membrane Proteins – allows large substances in cell – located in lipid bilayer – made of amino acids which contain polar and non-polar sides • Non-polar repelled by water on both sides of bilayer, this holds proteins in place. – proteins able to move along bilayer Fluidity of Membranes Membrane movement animation • Phospholipids and proteins in plasma membrane can move (drift lateally) within bilayer • This ability for the cell membrane to be fluid is called the Fluid Mosaic Model