* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Hedgehog signaling pathway wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Secreted frizzled-related protein 1 wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical cascade wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
From the dark side of fibronectin...
to the knowledge that FN is
essential in creating life
Rikke Brogaard, Benjamin Mintz, Chris Blum, Dev Patel, and Sage Foley
Objectives
1) Learn experimental techniques for use in
cell culture analysis [Level 2: Understand]
2) Analyze ways to manipulate a signaling
pathway [Level 4: Analysis]
3) Use your knowledge of methods to
discuss an experiment [Level 3: Application]
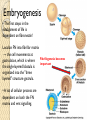
Embryogenesis
• The first steps in the
establisment of life is
dependent on fibronectin!
Localize FN into fibrillar matrix
→ the cell movements at
gastrulation, which is where
the single-layered blastula is
organized into the "three
layered" structure gastrula.
• A lot of cellular process are
dependent on both the FN
matrix and wnt signalling.
Fibrillogenesis becomes
important
Fibronectin is… Good?
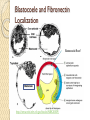
Blastocoele and Fibronectin
Localization
Bastocoele Roof
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK28309/
Stage 10 Xenopus
~6.4 hours into gestation
What might ‘stages’ be in embryology?
Cell Biology
What is the difference between a
dominant negative and a knockout?
What is a protein further down the
signaling chain from the protein of
interest called?
Activity 1 (10 min)
Utilizing the ‘tools’ commonly available to cell
biologists, develop an experiment to
determine which pathway is behind regulation
of the Reeses gene.
Milk
Chocolate
Ploppg
Desertegrin
Cocoa
Peanuts
Reeses
Wnt’s!
Combination of ‘Wingless’ and ‘Int’
Present in all animals
Cell signaling
Embriogenesis
Body Axis Signaling
◦ Dorsal Marginal Zone
Morphogenic Signaling
◦ Dorsal Marginal Zone
Dorsal Marginal Zone
Wnt Signaling
DIX
DEP
http://hormones.gr/preview.php?c_id=194
Figure 1
What is different in these pictures?
What was the purpose of each dn or
knockout and why were they all necessary
to determine the correct pathway?
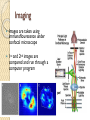
Traction Force Microscopy (TFM)
Basic Understanding
TFM is used to show stress on the
ECM
Beads are placed within a
polyacrylamide gel as reference
points
Fibronectin added to gel to
facilitate cell movement
1st image taken: Gel with cells
growing and deforming beads
2nd image: Cells removed leaving
only beads
Imaging
Images are taken using
immunoflourecence under
confocal microscope
1st and 2nd images are
compared and run through a
computer program
How is force calculated from these
images?
Images are compared to each other using Fourier
transform (FT) traction cytometry software
Math is beyond the scope of this class
Ex: minF {|↔G F − u|2 + λ2| F|2}.
Output can either be a topographic map or a
traction stress graph as seen later
Optimization of traction force microscopy for micron-sized focal adhesions
http://squishycell.uchicago.edu/papers/Stricker-JPCM-2010.pdf
Cadherins
Transmembrane
proteins
723 and 748 amino
acids long
Proteins critical in
cellular adhesion
Like binds to like
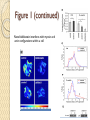
Figure 1 (continued)
Note: blebbistatin interferes with myosin and
actin configurations within a cell
Figure 3
What does this figure
show?
Over expression of C-cad
causes increased surface
area and less circular shape
of cells
Why?
Cadherins increase cell
adhesion altering cell
migration and clustering
Illustrates that traction
stress is increased in
clusters in comparison to
single cells
Immunofluorescence
Technique for staining molecules with
antibodies
What could be done if the primary
antibodies did not given enough
expression?
Indirect (secondary). Antibody is tagged
to the molecule and then the antibody
carrying fluorescence is tagged to first
antibody.
Activity 2 (10 min)
Make small groups and discuss Figure 2.
What is the purpose of this figure?
What results did they find?
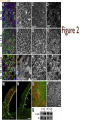
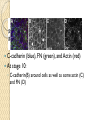
Figure 2
C-cadherin (blue), FN (green), and Actin (red)
At stage 10:
◦ C-cadherin(B) around cells as well as some actin (C)
and FN (D)
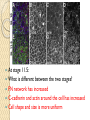
At stage 11.5:
What is different between the two stages?
FN network has increased
C-cadherin and actin around the cell has increased
Cell shape and size is more uniform
At stage 10 with N-cadherin:
What happens?
FN matrix is increased
Actin is increased
Rate of development is not increased
At stage 10:
◦ Red – N-cad; green – FN
What happens here?
M has N-cadherin and more FN is seen in
between cells than N, which is normal and has
FN around cells
At stage 11:
◦ O – has a dominant negative C-cad construct
(red); FN is green
◦ P – normal embryo
What is being shown?
O – FN is present but not formed matrix
unlike P which shows FN matrix which means
that cadherin is needed for FN matrix
assembly
What is being shown and why is it important?
Over-expressing C-cad dramatically increases
cadherins and does not change B-1 integrin
receptors
Dominant negative C-cad slightly reduces cadherins
and B-1 receptors which contributes to lower FN
fibrils
Cell-cell adhesion is regulated through changes of
adhesive activity rather than expression.
Shows that the antibodies used worked with the
proteins that were tagged
Figure 2: Cadherin Adhesion Regulates FN Fibril
Assembly
Do the cadherins do this alone?
What would be the logical next step?
Small GTPases are known to play key roles in
regulating adhesion and the cytoskeleton
Signal Transduction
(and Rho)
Rac and Rho are
small GTPases!!!
Rac and Wnt
Rac is downstream
of Dishevelled
Method
Dominant negative: mutations that act
against the wild-type allele
DN Rac and Rho were coinjected with
myc epitope-tagged N-cad into one cell
of the 2-cell-stage embryos
Cultured to stage 10: 1024 cells
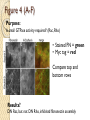
Figure 4 (A-F)
Purpose:
Is small GTPase activity required? (Rac, Rho)
• Stained FN = green
• Myc tag = red
Compare top and
bottom rows
Results?
DN Rac, but not DN Rho, inhibited fibronectin assembly
Figure 4 G
Western Blot!
What is β-actin??
What does this show?
• Dominant negative
Rac and Rho were
both being expressed
at equivalent levels
Figure 4 Take Home
Rac Activity is Required for
Cadherin to Promote FN Assembly
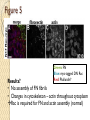
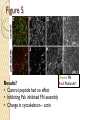
Figure 5
Is contribution of
Rac to fibronectin
assembly under
normal conditions?
Figure 5
Green: FN
Blue: myc-tagged DN Rac
Red: Phalloidin*
Results?
• No assembly of FN fibrils
• Changes in cytoskeleton – actin throughout cytoplasm
Rac is required for FN and actin assembly (normal)
Signal Transduction
(and Rho)
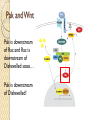
Pak and Wnt
Pak is downstream
of Rac and Rac is
downstream of
Dishevelled sooo…
Pak is downstream
of Dishevelled!
Examine Involvement of PAK
Blocked Pak function with an
inhibitory peptide
Control peptide
Figure 5
Results?
• Control peptide had no effect
• Inhibiting Pak inhibited FN assembly
• Change in cytoskeleton – actin
Green: FN
Red: Phalloidin*
Figure 5
Control peptide
Pax peptide
Results?
• Embryos developed normally with control peptide,
developed abnormally with Pax peptide
Figure 4 Take Home
Results
Dominant Negative Rac:
No assembly of FN fibrils
Changes in cytoskeleton – actin
throughout cytoplasm
Pak Inhibiting Peptide:
Inhibited FN assembly
Change in cytoskeleton – actin
Embryos develop abnormally
Figure 4 Take Home
Rac and Pak activity are each required
for fibronectin fibril assembly
Pak is required for normal development
of the Xenopus embryo
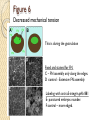
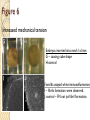
Figure 6
Show if the mechanical tension in BCR
(blastocoel roof) regulates FN assembly.
Reduce the hydrostatic pressure inside the BCR
by making a hole – ”deflate” the embryo.
Figure 6
Decreased mechanical tension
This is during the gastrulation
Fixed and stained for FN
C – FN assembly only along the edges.
D :control - Extensive FN assembly.
Labeling with anti-α5-integrin,pAb 881
E- punctured embryos rounder.
F:control – more edged.
Figure 6
Increased mechanical tension
Embryos inserted into mesh 1x1mm
G – causing cube shape
H:control
Fixed & assayed white immunofluresence
I – fibrils formation were observed.
J: control – FN not jet fibril formation.
The difference between matrix
assembly in cells (ex. fibroblast) and
in the BCR.
Tension is generated in order to
get FN dimer to fibrillogenesis.
Generated through cell attachment
cytoskeletal ancoring via focal
adhesions.
In blastocoel its 3D multilayered
microinvironment and the PCP
pathway upregulate FN matrix by
cadherin adhesive activity.
Final Activity (25 min.)
Objectives
1) Learn experimental techniques for use in
cell culture analysis [Level 2: Understand]
2) Analyze ways to manipulate a signaling
pathway [Level 4: Analysis]
3) Use your knowledge of methods to
discuss an experiment [Level 3: Application]