* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Molecules to Eye Color - Springfield School District
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Comparative genomic hybridization wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic transcription wikipedia , lookup
DNA sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Holliday junction wikipedia , lookup
Agarose gel electrophoresis wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Maurice Wilkins wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Transformation (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
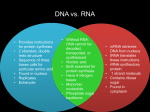
Molecules to Eye Color DNA, RNA and Protein Synthesis (Chapter 8) DNA Deoxyribonucleic Acid Carries genetic information Found every cell Discovery of DNA Structure: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sf0YX nAFBs8&safe=active Structure Composed of chains of nucleotides Nucleotides have 3 parts Phosphate Deoxyribose sugar Nitrogen base 4 kinds- G,C,T,A Chains have a “backbone” of phosphates and deoxyribose sugars Nitrogen bases sticking out Nitrogen Bases DNA is double stranded Another chain lines up with the nitrogen bases of the first G pairs with C and T pairs with A The bases (and strands)are held together by hydrogen bonds This forms a ladder shape ladder is twisted forming a double helix DNA DNA “Unfolding DNA” Fold a piece of notebook paper into four columns DNA Replication Makes 2 identical strands of DNA An enzyme called DNA polymerase “unzips” the two strands by breaking the H-bonds. Nucleotides with complimentary bases are attached to the exposed strands (If G is exposed, a C will be attached) This results in 2 identical strands RNA Brain Pop! Ribonucleic acid Functions in turning DNA code into proteins 3 types Messenger, mRNA Transfer, tRNA Ribosomal, rRNA Structure Chains of nucleotides 3 main differences between DNA and RNA 1. Ribose sugar (not deoxyribose) 2. Has U (uracil) instead of T (thymine) 3. Single strand (not double) Protein Synthesis Converting Proteins DNA code into proteins are composed of chains of amino acids (AA) Transcription mRNA is created from DNA 1. Section of DNA (gene) unzips 2. RNA nucleotides are paired with exposed bases Unfolding DNA to mRNA mRNA strand leaves the nucleus DNA zips back up Codon- 3 base sequence of mRNA Anticodon- 3 base sequence on the tRNA Translation mRNA codons are matched with tRNA anticodons. This places AA’s in a specific order. AA’s bond together as tRNA release Creating a chain of AA’s with a specific sequence Chains of AA’s = protein