* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download No Slide Title
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Transposable element wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Short interspersed nuclear elements (SINEs) wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Long non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in learning and memory wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcription factor wikipedia , lookup
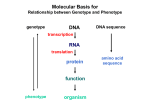
Molecular Basis for Relationship between Genotype and Phenotype genotype DNA DNA sequence transcription RNA translation protein function phenotype organism amino acid sequence Eukaryotic Gene Regulation - Transcription Expression of genes can be: - constitutively on (housekeeping genes ... ~15,000 in humans) - regulated (temporally or spatially ... up to 2000+ unique proteins in differentiated cell) Differentiation is a manifestation of genes being selectively turned off. Regulation of gene expression involves: - cis-acting regulatory elements - trans-acting transcription factors Transcription Factors Transcription factors have: 1. DNA binding domain (interact with promoter-proximal elements or enhancers/silencers) 2. Transactivation domain (activate or repress transcription, involved in protein/protein interaction) Structural Families of Transcription Factors and Regulatory Proteins: Helix-Turn-Helix: Many homeotic genes code for TF's of this class. Zinc-Finger: Many steroid hormone receptor protein TF's belong to this class. Leucine Zipper: Proto-oncogenes such as c-jun and c-fos are genes that encode TF's of this class. Helix-Loop-Helix: Certain proto-oncogenes and genes involved in differentiation encode TF's of this class. Structural Families of Transcription Factors and Regulatory Proteins: Zinc-Finger: Leucine Zipper: Helix-Loop-Helix: Enhanceosomes and Synergistic Effect on Transcription Enhanceosome: protein complex of trans-acting factors bound to appropriate DNA sequences. Proteins interact synergistically to elevate transcription rate. In b-interferon gene transcription, TFs recruit a coactivator (CBP) which is needed for transcription to occur normally. Formation of the enhanceosome and activation of RNA polymerase by coactivator are necessary for efficient transcription. Transcription of b-interferon gene is activated during viral infection. Tissue-specific Regulation of Transcription Regulated transcription depends on: - specific enhancer for gene(s) - enhancer-specific activator proteins - correct interaction between enhancer and activator Tissue-specific regulation requires that the enhancer-specific activator is present only in cells of that tissue type. : expression in an abnormal location “Master Switch” Gene Eye formation requires over 2000 genes. eyeless (ey) mutation causes small rudimentary eyes to form in Drosophila melanogaster. Small eyes (Sey, Pax-6) in mouse causes similar phenotype. Aniridia gene in human (lack of normal iris) shows considerable homology to ey gene. Comparison of ey+ and ey Phenotypes Wild-type eyes eyeless (ey) eyes size of ey eyes “Master Switch” Gene Wild-type eyeless (ey) gene can be induced to be expressed ectopically. eyeless (ey) gene codes for a helix-turn-helix transcription protein.