* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Biology
Survey
Document related concepts
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Model lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
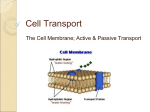
The Cell Movement Across the Membrane Cell Diagram: College of Dupage Quiz • 1. What is the type of bond within a single water molecule? • 2. A carboxyl group is symbolized by what? • 3. Briefly explain what happens in a hydrolysis reaction. • 4. Is maltose a monosaccharide, disaccharide, lipid, or protein? Quiz cont. • 5. Are lipids hydrophobic or hydrophilic? • 6. What is the difference between a saturated vs unsaturated fatty acid? • 7. What does the secondary structure of protein refer to? • 8. How does an enzyme work? Quiz cont. • 9. What is the difference between filtration and diffusion? • 10. What happens to a rbc in a hypertonic solution? • A hypotonic solution? C. Fluid Mosaic Model Plasma membrane is oily film made of lipids with diverse proteins embedded in Phospholipid bilayer – Hydrophillic heads facing water on either side of cell membrane – Hydrophobic tails directed to center Proteins -integral or transmembrane -peripheral Plasma Membrane www.susanahalpine.com/anim/Life/memb.htm Functions of the Cell Membrane • Defines boundaries of the cell • Governs interactions with other cells • Controls passage of materials into and out of cell III. Movement Across Membrane A. Selective Permeability Depends on 1. Size of particle 2. Solubility in lipids 3. Charge on particle 4. Carrier molecules in membrane Movement across membrane occurs through: • • • • Lipid bilayer Membrane channels With carrier molecules In vesicles Passive vs. Active Transport Requires ___________ • Primary Active Transport • Secondary Active Transport B. Non-mediated Transport Mechanisms 1. Diffusion 2. Osmosis 3. Filtration • Passive • Requires no energy Concentration Gradient B. Non-Mediated Transport Mechanisms DIFFUSION = when molecules move from a higher to a lower concentration. What type of things might affect the rate of diffusion? a. Magnitude of concentration gradient b. Temperature c. Size of diffusing particles d. Viscosity (thickness) of solvent Diffusion Animation: biologycorner.com Diffusion Osmosis: Diffusion of water across the membrane Water moves from an area of more water to an area of less water Osmotic Pressure Whenever dissolved substances such as glucose or protein are confined in a space by a selectively permeable membrane, they can pull water into the compartment by osmosis. The strength of the osmotic pull is directly related to the concentration of the solution. The greater the concentration, the greater the pulling, or osmotic pressure. Tonicity =the ability of a solution to affect fluid volume and pressure within a cell Environment surrounding cells may contain amounts of dissolved substances (solutes) that are… equal to less than greater than …those found within the cell. Tonicity Isotonic: no net movement of water between cell and environment Hypertonic: a higher concentration of solute. Hypotonic : a lower concentration of solute. Water will always move toward a hypertonic environment!! Diagrams: Cell: College of DuPage Osmosis - www.scienceaid.co.uk/biology/plants/osmosis.html Blood Cells: Mariana Ruiz Effects of tonicity on RBCs: Water moves from an area of more water to an area of less water www.tvdsb.on.ca/WESTMIN/science/sbi3a1/cells/Osmosis.htm Effects of Tonicity on RBCs Isotonic solutions: normal saline (0.9% NaCl), 5%D/W, and Ringer’s solution Under special conditions, hypotonic or hypertonic solutions may be administered IV. Most IV solutions are isotonic. Filtration- due to a pressure gradient Mediated Transport Mechanisms Characteristics 1. Specificity- carrier exhibits specificity for certain ligand, just as an enzyme does for its substrate 2. Saturation- once all carriers occupied, adding solutes will not make the process go any faster Three types 1. Facilitated Diffusion 2. Active Transport 3. Bulk Transport Facilitated Diffusion Passive -Proteins assist in diffusion of molecules across plasma membrane. -Movement only occurs in the presence of a concentration gradient. -Some molecules move across the membrane more quickly if diffusion is facilitated by a carrier molecule. Web References www.susanahalpine.com/anim/Life/memb.htm www.northland.cc.mn.us/biology/biology1111/animations/passive3.swf http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/chapter2/animation_how_osmosis_works.html www.tvdsb.on.ca/WESTMIN/science/sbi3a1/cells/Osmosis.htm www.education.uoit.ca/lordec/ID_LORDEC/capillary_fluid/capillary_fluid_LO.swf http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/chapter2/animation_how_facilitated_diffusion_works.html Review What are three examples of non-mediated transport mechanisms? Review What are three examples of non-mediated transport mechanisms? 1. Diffusion 2. Osmosis 3. Filtration Review What are three examples of non-mediated transport mechanisms? 1. Diffusion 2. Osmosis 3. Filtration Are these active transport or passive transport? Review 1. Osmosis is best defined as the movement of A) molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration B) molecules from an area of low concentration to an area of higher concentration C) water molecules across a membrane from an area of low water concentration to an area of higher concentration D) water molecules across a membrane from an area of high water concentration to an area of lower concentration 2. A red blood cell placed in a hypertonic solution will A) B) C) D) Expand Burst Shrink Have no change in shape 3. Facilitated diffusion requires A) Enzymes B) Carrier proteins C) lipid carriers D) carbohydrate carriers Review • The main difference between filtration and diffusion is Active Transport Transport of solute across membrane up (against) concentration gradient Analogous to a pump moving water uphill. ATP Driven Active Transport Energy from adenosine triphosphate (ATP) drives substances across the plasma membrane with the aid of carrier molecules. Examples: Sodium-potassium pump, bring amino acids into cell, pump Ca2+ out of cell Diagram: Cell, College of DuPage Sodium-Potassium Pump • Needed because Na+ and K+ constantly leak out of the cell • One ATP utilized to exchange three Na+ pushed out for two K+ brought in to cell Functions of Na+ K+ Pump • Regulation of cell volume • Heat production (thyroid hormone increases number of pumps; heat a by-product • Maintenance of membrane potential in all cells • Secondary active transport (no ATP used) Vesicular Transport • Transport large particles or fluid droplets through membrane in vesicles (uses ATP) • Exocytosis • Endocytosis – Phagocytosis – Pinocytosis – Receptor mediated endocytosis Phagocytosis = Cell Eating Pinocytosis= Cell Drinking Taking in droplets of ECF – Occurs in all human cells Membrane caves in, then pinches off into the cytoplasm as pinocytotic vesicle Transcytosis Transport of a substance across a cell Capture on one side and release on the other side Receptor mediated endocytosis moves it into cell and exocytosis moves it out the other side Receptor Mediated Endocytosis Exocytosis