* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 5 - Richsingiser.com
History of molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Expression vector wikipedia , lookup
Protein (nutrient) wikipedia , lookup
Ancestral sequence reconstruction wikipedia , lookup
Circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides wikipedia , lookup
Homology modeling wikipedia , lookup
Protein domain wikipedia , lookup
Protein folding wikipedia , lookup
Interactome wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Intrinsically disordered proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
Protein purification wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
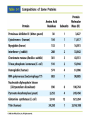
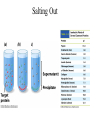
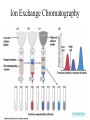
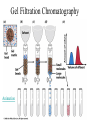
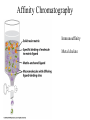
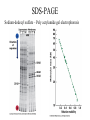
Fundamentals of Biochemistry Third Edition Donald Voet • Judith G. Voet • Charlotte W. Pratt Chapter 5 Proteins: Primary Structure Copyright © 2008 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Section 1 – Polypeptide Diversity Insulin primary structure Primary Structure – linear sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain 20100 = 1.27 x 10130 possible combinations 9 x 1078 atoms estimated in universe Section 2 – Protein Purification • Purification was difficult for a endogenous protein – First proteins studies were very abundant • Modern cloning techniques all for production of large quantities of specific proteins – This process still requires that the protein be isolated from a cell, and purified from the other cellular components Conditions affect protein Stability • pH – The wrong pH causes denaturation • Temperature – The wrong temperature can cause denaturation • Presence of other proteins – Proteases can destroy proteins • Adsorption to surfaces – Some proteins can be denatured upon exposure to air • Long term storage – Most proteins should be stored at -20°C or lower to minimize degradation and denaturation ELISA Enzyme linked immunosorbent assay Used to determine (quantify) the amount of protein present Animation Spectroscopic method for determining protein concentration Beer-Lambert law A=εcl A280 – absorbance of F, Y, W Colorimetric method for determining protein concentration Bradford assay Salting Out Ion Exchange Chromatography Animation Gel Filtration Chromatography Animation Affinity Chromatography Immunoaffinity Metal chelate SDS-PAGE Sodium-dodecyl sulfate – Poly acrylamide gel electrophoresis Capillary Electrophoresis 2D Gel electrophoresis Section 3 – Protein Sequencing • Important to know the sequence of a protein – Primary structure dictates shape – Evolutionary comparisons can be made – Diseases arise from mutations of primary structure Step 1. Step 2 Step 3 Step 4 Edman Degradation Animation Section 4 – Protein Evolution Protein Evolution • Homologue – evolutionarily similar proteins within the same species – Invariant residue – identical aa among homologues – Conserved residue – similar (class) aa among homologues – Hypervariable residue – no similarity among homologues Protein Evolution • Domain – region of proteins that have very similar folding patterns (40-200 aa) • Orthologues – homologous proteins in different species • Paralogues – independently evolving genes in the same species • Pseudogenes – duplicated gene that are not expressed All problems at end of chapter except 6, 13, and 19 You have isolated a decapeptide (10 residues) called FP, which has anticancer activity. Determine the sequence of the peptide from the following information. 1. One cycle fo Edman degradation of intact FP yields 2 mole of PTH-aspartate per mole of FP. 2. Treatment of a solution of FP with 2-ME followed by the addition of trypsin yields three peptides (Ala, Cys, Phe) (Arg, Asp) (Asp, Cys, Gly, Met, Phe) The intact (Ala, Cys, Phe) peptide yields PTH-cysteine in the first cycle of Edman degradation. 3. Treatment of 1 mol of FP with carboxypeptidase (cleaves at Cterminus of all residues) yields 2 mol of phenylalanine. 4. Treatment of intact pentapeptide (Asp, Cys, Gly, Met, Phe) with BrCN yields two peptides with composition (homoserine lactone, Asp) and (Cys, Gly, Phe) The (Cys, Gly, Phe) peptide yields PTHglycine in the first cycle of Edman degration.