* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download - Toolbox Pro
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
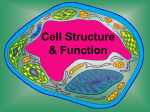
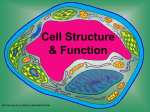
Cell Organelles The Parts Inside of a Cell A Look Inside the Cell Each cell contains smaller parts Organelle = tiny cell structure that carries out a specific function within the cell Surrounding the Cell Cell Membrane (a.k.a. Plasma Membrane) Outer membrane of cell that controls what comes into and out of the cell Allows good stuff in and lets wastes out of cell “gateway” of the cell Cell Membrane is a screen What does a window screen do? What things are kept out of a window screen? What things can get in a window screen? A screen is similar to the cell membrane in a cell. Cell Wall http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html Not all cells have cell wall! Most commonly found in plant cells & bacteria Not in animal cells Supports & protects cells Inside the Cell – The Center Nucleus Cell’s control center – directs cell’s activities Separated from the rest of the cell by nuclear membrane Contains genetic material – DNA BRAIN of the cell Inside the Cell – In the Cytoplasm Cytoplasm Gel-like mixture that constantly moves Between cell membrane and nucleus Holds organelles Site for chemical reactions Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html Moves materials around in cell Smooth type: lacks ribosomes Rough type (pictured): ribosomes embedded in surface Like the highway system for the cell Ribosomes Make proteins Each cell contains thousands Found on endoplasmic reticulum & floating throughout the cell “Factories” for the cell http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html Mitochondria Convert energy in food molecules (sugars) to energy (ATP) the cell can use to carry out its activities “Powerhouse” or “Energy Plant” of cell http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html Golgi Bodies or Golgi Apparatus Looks like stacked “pancakes” Protein 'packaging plant' Move materials within the cell Move materials out of the cell Like the “UPS store” for the cell http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html Lysosome Contains chemicals that breaks down some materials in cell “janitor” for the cell http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html Vacuoles Provide storage for cell Store materials needed for cell Also store wastes for cell http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html Chloroplast Usually found in plant cells (Autotrophs) Contains green chlorophyll Where photosynthesis takes place Captures energy from sunlight to make energy for cell http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html