* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download chromosome sister copy centromere
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Kinetochore wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Spindle checkpoint wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
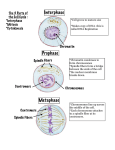
The Cell cycle: • Just as you have a distinct life cycle, so do cells. • You spend most of your life growing and maturing, and only a small portion of your life reproducing. • The same is true for cells. INTERPHASE • Phase between cell division • Cell grows • DNA is uncoiled and invisible (chromatin) • DNA copied The process of cell division is called: • Mitosis • “I hit my toe sis!” • The mitosis consists of many different stages The most important part of cell division: • Making sure the right number chromosomes end up in both cells • You have 46 chromosomes in every cell • Thus each cell must make a copy of each chromosome before it divides Mitosis Stage 1: PROPHASE • nuclear membrane breaks down • Chromatin wind to become visible chromatids • chromatids (pairs of chromosomes) stay attached by a centromere. • Centrioles (poles) appear and move to opposite sides of cell • Spindle fibers form between poles Chromatids • Two identical chromosomes joined at a centromere CHROMOSOME CENTROMERE SISTER COPY Stage 2: Metaphase • Chromotids attach to spindle fibers • Chromotids line up on midline (equator) of cell (meet in middle) Stage 3: Anaphase • Chromatids separate and move to opposite ends of the cell • Centromere splits in half Stage 4: Telophase • Spindle disappears • Chromosomes unwind and become less visible • Nuclear membranes form around the new sets of chromosomes • Cell begins to pinch into two • Mitosis ends Cytokinesis • The division of the rest of the cell organelles roughly in half • Two daughter cells are completely formed How to remember the order: • • • • • • I Pee on the M A T C (see) Assignment: • P 25-26 in the workbook Q#1-12