* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download C8-Cellular Transport
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
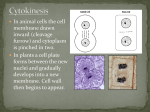
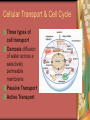
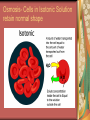
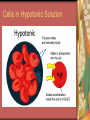
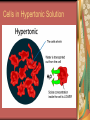
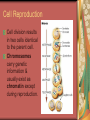
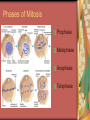
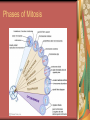
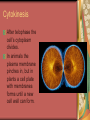
C8-Cellular Transport And the Cell Cycle Contents Section 1- Cellular Transport & the Cell Cycle Section 2- Cell Growth & Reproduction Section 3- Control of the Cell Cycle Cellular Transport & Cell Cycle Three types of cell transport Osmosis diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane Passive Transport Active Transport Osmosis- What controls it? Concentration gradient Water diffuses until it is in equal concentration on both sides of a membrane. Random movement due to kinetic energy Osmosis- Cells in Isotonic Solution retain normal shape Cells in Hypotonic Solution Cells in Hypertonic Solution Effects on Animal or Plant Cells Passive Transport PT does not require energy Either simple diffusion or facilitated diffusion across a membrane through a transport or carrier protein. Active Transport Contrast passive & active Passive transport acts with the concentration gradient and requires no energy to move from higher to lower concentration. Active transport acts against the concentration gradient and requires energy to move from lower to higher concentration. Transport of Large Particles Endocytosis cell process to engulf material & create vacuole Exocytosis expulsion or secretion of waste or hormones from the cell Both processes require energy. 8.2 Cell Growth & Reproduction Diffusion limits cell size. It’s fast & efficient over short distance. Slow rate over longer distance. Amount of DNA must support protein needs of the cell. Surface area to volume ratio- volume increases faster than surface area i.e. double area = 8X volume 8.2 Cell Growth & Reproduction Cells divide before they become too large to function properly. Cell Reproduction Cell division results in two cells identical to the parent cell. Chromosomes carry genetic information & usually exist as chromatin except during reproduction. The Cell Cycle Sequence of growth & division Majority of cycle is growth phase called Interphase. Protein production Chromosome duplication Mitosis period of nuclear division Phases of Mitosis Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Phases of Mitosis Prophase- chromatin coils to form visible chromosomes Metaphase- chromosomes move to the equator of spindle Anaphase- centromeres split and sister chromatids move to opposite poles. Telophase- Two distinct daughter cells are formed Phases of Mitosis Cytokinesis After telophase the cell’s cytoplasm divides. In animals the plasma membrane pinches in, but in plants a cell plate with membranes forms until a new cell wall can form. Results of Mitosis Guarantees genetic continuity Cellular organization-> tissues-> organs-> organ systems Organ systems work together for the survival of the organism 8.3 Control of the Cell Cycle Proteins & Enzymes control the cell cycle. Checkpoints within the cycle are controlled by proteins called cyclins and by kinase enzyme. Cancer Unrestrained cell division causing malignant growth Can be caused by environmental factors or by changes in enzyme production Control of the Cell Cycle Enzyme production is controlled by genes located on the chromosomes. Key checkpoint during interphase just before DNA replicates. Cancer: Mistake in Cell Cycle Cancerous cells form masses of tissues called tumors. Later cancer cells enter the bloodstream and metastasize to other parts of the body. A healthy lifestyle can reduce the incidence of cancer. Low-fat high-fiber diet, exercise, avoid tobacco use. Cancer Prevention Healthy Lifestyle Diet low in fat & high in fiber from fruits, vegetables and grains Vitamins A, C, E and mineral calcium Daily exercise Avoiding tobacco use























![MITOSIS WORKSHEET - New Page 1 [bs079.k12.sd.us]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/014668413_1-30813973b0cb9de17ced950a5cb16263-150x150.png)