* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cellular Transport and the Cell Cycle
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
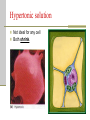
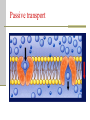
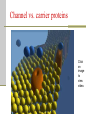
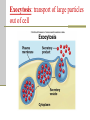
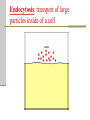
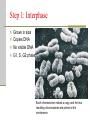
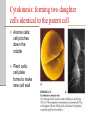
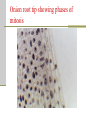
Cellular Transport and the Cell Cycle Unit 3 Chapter 8 Different ways of transporting materials across a cell membrane 1. Passive transport 1. 2. 3. Diffusion Osmosis: water diffusion Facilitated transport 2. Active transport 3. Exocytosis 4. Endocytosis Cells in isotonic solutions Cell loses and gains water at an equal rate. Net change to cell = nothing Isotonic solution Not ideal for plant cells because the cells become flaccid (limp) Ideal for animal cells or cells without cell walls Cells in a hypotonic solution More water moves into the cell than moves out. Net change = cell mass increases Hypotonic solution Ideal for plant cell where the cell becomes turgid (swollen) Not ideal for animal cells where the cell lyses (bursts) Cells in a hypertonic solution More water moves out of the cell than moves in Net change = cell mass decreases Hypertonic solution Not ideal for any cell Both shrink. Passive transport Movement of materials across a cell membrane in the direction of higher concentration to lower concentration No ATP energy required Passive transport by proteins Facilitated transport Movement of chemicals down a chemical gradient (from high to low concentration) through a protein Passive transport Channel vs. carrier proteins Click on image to view video. Active transport Requires energy to move substances across the membrane against the concentration gradient (from lower to higher concentration) Click on image to view video. Exocytosis: transport of large particles out of cell Endocytosis: transport of large particles inside of a cell Cell reproduction: making new cells by a process called cell division Cell cycle: sequence of growth and division of a cell Step 1: Interphase (G1, S, G2) Step 2: Mitosis and Cytokinesis (M) Eukaryotic chromosome structure Double helix coiled and twisted into a condensed structure Bacterial DNA differs in that it is circular and not linear. Step 1: Interphase Grows in size Copies DNA No visible DNA G1, S, G2 phases Each chromosome makes a copy, and the two resulting chromosomes are joined at the centromere. Step 2: Mitosis (nuclear division) Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Prophase: spindle fibers extend, nuclear membrane disintegrates, chromosomes coil up and pair up Metaphase: Meta means “middle”, chromosomes aligned along the middle Anaphase: chromosomes pulled apart when spindle fibers become shorter Telophase: two nucleus form at each pole of the cell Cytokinesis: forming two daughter cells identical to the parent cell Animal cells: cell pinches down the middle Plant cells: cell plate forms to make new cell wall Onion root tip showing phases of mitosis The cell cycle Click on image to view video.