* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Cell
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
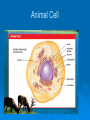
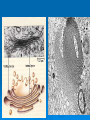
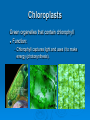
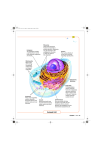
The Cell: The Basic Unit of Life The Cell The Cell has many parts. Each part has a specific job and plays an important part in the life of a cell. http://www.classzone.com/books/ml_science_share/vis_sim/chm05_pg7_ce ll/chm05_pg7_cell.html Animal Cell Warm Up ____ 1. Provides energy for the cell by breaking down glucose molecules. ____ 2. Converts light energy to chemical energy for the plant cell through photosynthesis. ____ 3. This organelle controls all cell activities. ____ 4. Is selectively permeable. ____ 5. A gelatin-like substance that is the site of many chemical reactions in the cell. Cell Membrane Structure: protective layer that surrounds the cell. Composed of lipids and phospholipids. Function: controls interactions between the environment and the inside of the cell. Cytoplasm Structure: Gelatin like substance inside cell, constantly flowing. Function: a) keeps the cell moist. b) allows for chemical reactions to take place. Cytoskeleton Structure: framework made up of thin hollow tubes. Function: Helps the cell maintain it’s shape Nucleus The brain of the cell Structure: has it’s own membrane. Functions: a) directs all cell activity b) contains the hereditary material (DNA) Mitochondria The POWER HOUSE of the cell!!!!! Function: breaks down nutrients to make energy for the cell. ATP is the energy source. *Why would muscle cells in your legs have more mitochondria than muscles in your abdomen? Ribosomes Made in the nucleolus and sent out to the cytoplasm. Structure: -Not membrane bound -Either float freely in the cytoplasm or are connected to the endoplasmic reticulum. Functions: -Produces protein using the information provided by the DNA. Ribosomes Endoplasmic Reticulum Made up of folded membranes Structure: either be rough or smooth -Rough: has ribosomes -Smooth: no ribosomes Functions: -Acts as the processing center for proteins and other substances. -A system of highways to send things to different places. Golgi Bodies Golgi Apparatus/Golgi Complex Structure: -Stacked membranes, acts as the mail center. Functions: -Sort out proteins and other substances in vesicles (packages) to go to their appropriate places (other parts of the cell, organelles, or out of the cell). Vacuoles Vacuoles: temporary storage for any excess cell material. Lysosomes Function: -Breaks down and recycles unused substances -Also kills the cell (Lysis) when the cell is no longer functional. Extra Plant Structures Plants are unique organisms and their cells have two added organelles. Cell Wall -Tough, rigid, outer coverings made of CELLULOSE (a carbohydrate) Function: -Protection -Support and shape for the plant Chloroplasts Green organelles that contain chlorophyll Function: • Chlorophyll captures light and uses it to make energy (photosynthesis). Different Types of Cells Nucleus- I’m the boss Mitochondrion- power packed Cytoplasm- oooey, gooey Membrane- coming or going Vacuole- hold on layaway Golgi Bodies- packed –n- ready Lysosomes- clean up the junk Ribosomes- one order o’ proteins ER- on the road again Cytoskeleton- keep’n the shape Chloroplast- green food machine Cell Wall- rough –n- tough http://www.classzone.com/books/ml_science_share/vis_sim/chm05_pg19_microscop e/chm05_pg19_microscope.html