* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Growth
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
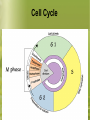
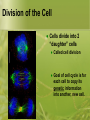
Warm-Up # 4 1/8/13 1) What is the difference between haploid and diploid? 2) What are the two types of cell division? 3) How is meiosis different from mitosis? 4) Label the pictures below. Grade Sheet 1/8/13 Unit 6 Vocab Quiz Limits to Cell Growth, SA/V ratio and the Cell Cycle Unit 6 Cellular Reproduction What are we learning? Essential Question Objectives: What happens to cells when you grow or get injured? Understand why a cell divides Limitations to cell growth Evaluate surface area to volume ratio Understand the cell cycle Fact: Sitting in the room….listening to me ramble on, you have lost 40,000 skin cells. But, you’re not naked. Why? Cells reproduce We get bigger by producing more cells, not bigger cells (SIZE DOESN’T MATTER!!!) Limits to Cell Growth Larger a cell becomes, more demands the cell places on its DNA. A large cell has trouble moving nutrients and waste across the membrane “Limits” DNA “Overload” Cell is small demand is met Cell is big information crisis “Cell Phone Towers” Exchanging Materials Food, oxygen, water enter waste leaves Rate at which the exchange takes place depends on the surface area of the cell (total area of the cell membrane) Ratio of Surface Area to Volume Volume increases much more rapidly than surface area (water balloon bursting) This causes a decrease in the ratio of surface area to volume (closer to 1) Therefore cells must divide Ratio of Surface Area to Volume in Cells Cell Size Surface Area (length x width x 6) Volume (length x width x height) Ratio of Surface Area to Volume Cell Growth 1. 2. Which cell is smaller; 10:1 or 6:1? Which cell is more likely to divide; 2:1 or 3:1? Remember!!! The surface area to the volume ratio gets smaller as the cell gets larger. Cell Cycle Division of the Cell Cells divide into 2 “daughter” cells Called cell division Goal of cell cycle is for each cell to copy its genetic information into another, new cell. Starts With… Two general periods… Period of Growth—Interphase Cell grows in size and carries on metabolism Chromosomes duplicate in preparation for Mitosis (Each cell must copy its genetic information) Period of Division(Mitosis)—nucleus and then its cytoplasm divides Interphase—A Busy Time Making ATP Repairing Themselves Excreting Waste Making Proteins Producing New Organelles Interphase Stages G1 phase S phase G2 phase Interphase Breakdown G1Cell Grows Protein Production is High SG2Chromosomes Mitochondria copy and other organelles are manufactured Preparation for mitosis Lets Review: Give two reasons why cells divide. As a cell increase in size, which increase more rapidly, its surface area or its volume? Warm-Up #3 1) 2) 3) 4) 1/6/12 What are the two periods a cell goes through in the cell cycle? Which period takes longer? Give two reasons a cell would not want to get big, but divides instead. If a cell has a height of 5 cm, a width of 5 cm and a length of 5 cm, what is its surface area? Cell Cycle Cut-Out Cut out the all pieces on your paper Glue the pieces to your circle like on the board Cut and glue the words on the cycle where they belong On the back: explain what each step in mitosis does Use pg. 155-157 to help you complete this Keep it in your folder to use on Monday’s quiz





























![The cell cycle multiplies cells. [1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/015575697_1-eca96c262728bdb192b5eb10f1093d3e-150x150.png)

