* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell parts powerpoint
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
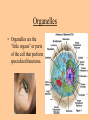
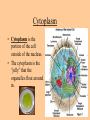
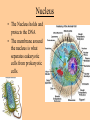
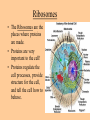
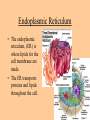
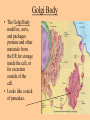
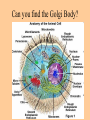
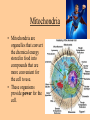
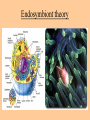
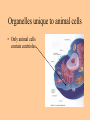
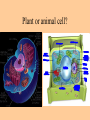
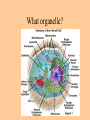
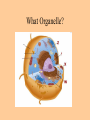
Cell parts Organelles • Organelles are the “little organs” or parts of the cell that perform specialized functions. Cytoplasm • Cytoplasm is the portion of the cell outside of the nucleus. • The cytoplasm is the “jelly” that the organelles float around in. DNA • The DNA is like the “brains” of the cell. • DNA controls what the cell does and when it does it. • DNA is tiny, but has a big impact on what you look like and what you are good at. (5 million DNA strands could fit on the head of a pin). Nucleus • The Nucleus holds and protects the DNA • The membrane around the nucleus is what separates eukaryotic cells from prokaryotic cells. Chromosomes • Chromosomes are short fat pieces of DNA that form during cell division. Ribosomes • The Ribosomes are the places where proteins are made. • Proteins are very important to the cell! • Proteins regulate the cell processes, provide structure for the cell, and tell the cell how to behave. Proteins • Proteins are all around you: – The most common protein in the world is called RuBisCO. It is used to do photosynthesis. – The most common protein in the human body (25-30%) is collagen, which is used for connective tissue, bone, muscle, etc… – A protein called Lactase helps you break down the sugar in milk. – Antibodies are proteins in your body that help fight disease. – Hemoglobin (that makes your blood cells red) is a protein. – A protein called melanin is responsible for skin/hair/eye color, and for moles, freckles, and tans. – Hair, horns, and fingernails are made of a protein called keratin. – A protein called catalase helps break down hydrogen peroxide in your blood Endoplasmic Reticulum • The endoplasmic reticulum, (ER) is where lipids for the cell membrane are made. • The ER transports proteins and lipids throughout the cell. Golgi Body • The Golgi Body modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and other materials from the ER for storage inside the cell, or for excretion outside of the cell. • Looks like a stack of pancakes. Can you find the Golgi Body? ER to the Golgi Lysosomes • Lysosomes are small organelles filled with enzymes to help digest, or break down, the “junk” in the cell. • These organelles are like the garbage men of the cell. Mitochondria • Mitochondria are organelles that convert the chemical energy stored in food into compounds that are more convenient for the cell to use. • These organisms provide power for the cell. Endosymbiont theory Cell Membrane • The cell membrane covers the entire cell and determines what is allowed in or out of the cell. Organelles Unique to Plants • Only plants have the following organelles: – Chloroplasts – Large vacuoles – Cellulose Cell wall Chloroplasts • Chloroplasts capture energy from the sun and allow the plant to do photosynthesis. • They contain chlorophyll, a pigment that reflects green light. Large Vacuoles • Large Vacuoles store material. • In a plant, vacuoles help pump water out of the cell if too much water enters. Cell Wall • The Cell wall is made of cellulose and provides support and protection for the cell. Plant cells • Because of their cell walls, plant cells are usually square-shaped. Organelles unique to animal cells • Only animal cells contain centrioles. Centrioles • Centrioles help organize cell division. Plant or animal cell? What organelle? What Organelle?