* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The cell theory states that: All living things are
Survey
Document related concepts
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
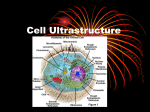
Cells & Organelles What is a cell? Basic unit of life that can carry out all the functions of a living thing. Various sizes and shapes Organism- living thing Unicellular Multicellular Microscope Development 1665 – Robert Hooke named cell 1674 – Anton von Leeuwenhoek looked at cells in pond water and blood and published his observations Cell Theory The cell theory states that: •All living things are composed of cells •Cells are the basic unit s of structure and function in living things •New cells are produced from existing cells Cells from Labs: Types of Cells Prokaryotic cell Eukaryotic cell Prokaryotic Cells Prokaryotic Cells: have genetic material that is NOT contained in a nucleus that is; they lack nucleus Simple cell No membrane-bound organelles Chromosome not contained in nucleus Small cells Ex – ONLY bacteria Eukaryotic Cells Eukaryotic cells contain a nucleus in which genetic material is separated from the rest of the cell. That is; they have membrane bound nucleus – – – – – Complex cell Membrane-bound organelles Chromosomes contained in nucleus Larger cells Ex – all other organisms (NOT bacteria) PARTS OF A CELL Plasma (cell) membrane Cell Wall Cytoplasm Nucleus Nuclear membrane Ribosomes Endoplasmic Reticulum Golgi Apparatus Mitochondria Lysosome Vacuole Chloroplasts The Plasma Membrane is like the SKIN of the cell. •The Cell Membrane controls what enters and leaves the cell. Selective permeablility-allows only certain materials to pass through Copyright © Arizona Board of Regents http://www.biology.arizona.edu The Nucleus is like the BRAIN of the cell. • The nucleus is the control center of the cell. • It contains the genetic information for the cell in the form of DNA called chromatin. Nucleolus and Nuclear Membrane • Nucleolus- produces ribosomes. • Nuclear membrane-seperates nucleus from the cytoplasm. The Mighty The “Mighty” Mitochondria is the POWERHOUSE of the cell. •Mitochondria - Makes energy in the form of ATP • ATP are produced to “power” the cell. The Endoplasmic Reticulum is the cells DELIVERY SYSTEM. •Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) Delivers proteins. •A tubular system connecting the nuclear membrane to the cell membrane. The Golgi Apparatus is the PACKAGING CENTER of the cell. • Golgi Apparatus - Packages and modifies proteins. Vacuoles are the STORAGE SPACES for cells. • Store food, enzymes, wastes, and other materials needed by the cell. Copyright Tupperware Worldwide www.order.tupperware.com Lysosomes • Specialized vacuole that digest and break down waste. • The “garbage man” of the cell. Ribosomes • Protein synthesis (makes proteins) Cytoplasm • Jello-like substance where organelles are embedded. Centrioles • Centrioles help in cell division. • They are found only in animal cells. Organelle Diseases