* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Cell in Action
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
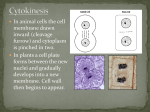
The Cell in Action • The exchange of materials between a Cell Membrane cell and its environment takes “The Gate Keeper” place at the cell’s membrane. • The cell membrane is semipermeable which means that only certain substances can pass through. • To understand how materials move into and out of the cell, you need to know about diffusion. What is Diffusion? • Diffusion is the movement of matter from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. • In this process, cells do not require energy because matter moves naturally in this way. • Diffusion happens within and between living cells. • The movement stops when a state of equilibrium is reached. • Diffusion is a form of passive transport because no energy is required. Ed, Edd n Eddy Example Ed, Edd and Eddy had the bright idea to ride a shopping cart down a hill, so they put Eddy in the cart and push him up the hill. Did this require energy? Yes! This task required a lot of energy because they had to work in order to push Eddy and the cart up the hill. They were pushing him from an area of low - to an area of high potential kinetic energy. (kinetic means energy of motion) • When they got to the top of the hill where the potential energy was high, they simply let go of the cart and Eddy flew down the hill and crashed! • Was work required to push Eddy down the hill? • No, because moving from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration happens naturally! (ex. heat transfer, potential kinetic energy, diffusion and osmosis) Osmosis • Osmosis is the diffusion of water through the semipermeable cell membrane. • Semipermeable means that only certain substances can pass through. • Osmosis is important to cells because a cell cannot function properly without adequate water. For example, red blood cells are surrounded by plasma. Plasma is made up of water, salts, sugars, and other particles. The concentration of these particles is kept in balance by osmosis. Water moves equally into and out of the cell. If red blood cells were in pure water, water molecules would flood into the cells and cause them to burst. When red blood cells are put into a salty solution, the concentration of water molecules inside the cell is higher than the concentration of water outside. This difference makes water move out of the cells, and the cells shrivel up. Osmosis also occurs in plant cells. When a wilted plant is watered, osmosis makes the plant firm again. Passive Transport • Passive transport moves small particles, such as sugars, cross the cell membrane through passageways called channels. • The movement of particles across the cell membrane without the use of energy is called passive transport. (ex. diffusion, osmosis) • During passive transport particles move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. Active Transport • Active transport moves large particles into and out of the cell using energy. • Large particles move into and out of the cell by processes called endocytosis and exocytosis. • ATP energy is needed! Endocytosis • Endocytosis is an active transport process by which a cell surrounds a large particle, such as a protein, and encloses it in a vesicle to bring the particle into the cell. Exocytosis • Exocytosis is an active transport process where large particles, such as waste, exits the cell. • During exocytosis a vesicle fuses with the cell membrane and releases the particle to the outside of the cell. Cell Energy Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Photosynthesis • Plants need water, carbon dioxide and sunlight for photosynthesis to take place. • Plants get the water they need through their roots and carbon dioxide from small opening under the leaf called stomata. • Plants have chloroplast, that are filled with a green pigment called chlorophyll. The chlorophyll absorbs sunlight to use for energy to produce glucose (sugar) during photosynthesis. • Photosynthesis produces glucose and oxygen. Cellular Respiration • • • • Animal cells get energy from food through a process called cellular respiration. Animals inhale oxygen which is needed to break down food (glucose) in the mitochondria and release large amounts of energy ATP to fuel cell activities. In plants, cellular respiration takes place in the cytoplasm. Cellular respiration produces carbon dioxide, water and ATP. The Cell Cycle • The cell cycle is the life cycle of a cell. • The cycle begins when the cell is formed and ends when the cell divides. • Cell division in prokaryotic cells is called binary fission, which means “splitting into two parts.” • The DNA ring and ribosomes are copied each new cell will have one copy. Life Cycle of a Eukaryotic Cell Eukaryotic cells divide in three stages: • Interphase • Mitosis • Cytokinesis Interphase (stage 1) • Chromosomes are copied. • Each chromosome becomes two chromatids. Mitosis (stage 2) There are four phases of Mitosis: • Prophase • Metaphase • Anaphase • Telophase Prophase (mitosis phase 1) • Chromosomes condense from long strands to rod like structures. Metaphase (mitosis phase 2) • The nuclear membrane is dissolved. • Paired chromatid align at the cell’s equator. Anaphase (mitosis phase 3) • The chromatid separate and move to opposite sides of the cell. Telophase (mitosis phase 4) • A nuclear membrane forms around each set of chromosomes. • Two nuclei are formed. Cytokinesis (stage 3) • In cells that lack a cell wall the cell pinches in two. Two new daughter cells are formed. • In cells with cell walls a cell plate forms between the two new cells. Animal and Plant Cell Cycle • http://iknow.net/player _window.html?url=med ia/prophase_video_aut o.swf&width=360&heig ht=285 http://iknow.net/player_w indow.html?url=media/pla nt_mitosis_auto.swf&widt h=360&height=285 Human DNA • Humans have 46 chromosomes. • 23 pairs of homologous chromosomes. • Homologous chromosomes are pairs of chromosomes that have the same sequence of genes and the same structure. Human Cell Cycle