* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CHAPTER 4 – The Cell In Action
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
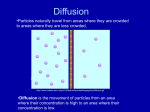
CHAPTER 4 – The Cell In Action A) Section 1: Exchange with the Environment “Through the Cell Membrane” 1) What Is Diffusion . . . 2) Osmosis—Diffusion of Water 3) The Cell Environments and Osmosis 4) Moving Small Particles—Comparing Active and Passive Transport 5) Moving Large Particles—Endocytosis and Exocytosis B) Section 2: Cell Energy 1) From Sun to Cell—Photosynthesis 2) Getting Energy from Food—Cellular Respiration 3) Linking Photosynthesis and Respiration 4) Fermentation C) Section 3: The Cell Cycle 1) The Life of a Cell—Cell Cycle 2) Chromosomes—Making More Cells 3) Homologous Chromosomes . . . Pg. 99 4) Mitosis—will ensure that each new cell receives an identical copy of each chromosome. OSMOSIS Particles move from The diffusion of water through a an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration Does not require ATP (energy) Water PASSIVE TRANSPORT Particles move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration Does not require ATP (energy) Sugar ACTIVE TRANSPORT Particles move from an area of low concentration to an area of high Particles move through proteins Requires ATP (energy) semi-permeable membrane. The water particles will move out of the cells to where water molecules are less concentrated in the salty solution; thus, the cells will shrink. The movement of substances across a cell membrane without the use of energy by the cell. Diffusion is when any kind of particles move from a crowded area to a less crowded area. The movement of substances across the cell membrane that requires the cell to use energy; b/c the cell must work against the flow of particles. Endocytosis and exocytosis are examples of active transport. In both processes the cell must change shape, wrap around a particle, and make other movements that require the cell to use energy.