* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Animal Cell
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
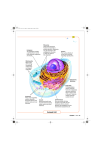
Does it pass MR. FUDRUG test? Cell Structures, Functions and Transport Two Types of Cells Prokaryotic •Eukaryotic • Prokaryotic Do not have structures surrounded by membranes Few internal structures One-celled organisms, Bacteria http://library.thinkquest.org/C004535/prokaryotic_cells.html Eukaryotic Contain organelles surrounded by membranes Most living organisms Plant http://library.thinkquest.org/C004535/eukaryotic_cells.html Animal Intro to the Animal Cell Cell Membrane http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html Outer membrane of cell that controls movement in and out of the cell Double layer Cytoplasm Gel-like mixture Surrounded by cell membrane Contains hereditary material Figure 7-5 Plant and Animal Cells Animal Cell Section 7-2 Cytoplasm Nucleolus Nucleus Go to Section: Cell Membrane Eukaryotic Cell Organelles and Function Nucleus 1. Nickname: “The Control Center” Function: holds the DNA 1. Nucleolus Spherical body in the nucleus of the cell containing RNA and produces ribosomes Figure 7-5 Plant and Animal Cells Animal Cell Section 7-2 Cytoplasm Nucleolus Nucleus Go to Section: Ribosomes Cell Membrane Eukaryotic Cell Organelles and Function Ribosomes 2. Function: makes proteins Found in all cells, prokaryotic and eukaryotic Eukaryotic Cell Organelles and Function Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) 3. Nickname: “Roads” Function: The internal delivery system of the cell Figure 7-5 Plant and Animal Cells Animal Cell Section 7-2 Cytoplasm Nucleolus Nucleus Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Go to Section: Ribosomes Cell Membrane Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Endoplasmic Reticulum 2 Types: 1. Rough ER: 2. Rough appearance because it has ribosomes Function: helps make proteins, that’s why it has ribosomes Smooth ER: NO ribosomes Function: makes fats or lipids Figure 7-5 Plant and Animal Cells Animal Cell Section 7-2 Cytoplasm Nucleolus Nucleus Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Golgi Complex Go to Section: Ribosomes Cell Membrane Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Eukaryotic Cell Organelles and Function Golgi Complex 4. Nickname: The shippers Function: packages, modifies, and transports materials to different location inside/outside of the cell Appearance: stack of pancakes Figure 7-5 Plant and Animal Cells Animal Cell Section 7-2 Cytoplasm Nucleolus Nucleus Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Golgi Bodies Go to Section: Ribosomes Cell Membrane Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Eukaryotic Cell Organelles and Function Lysosomes: circular, but bigger than ribosomes) 5. Nickname: “Clean-up Crews” Function: to break down food into particles the rest of the cell can use and to destroy old cells Figure 7-5 Plant and Animal Cells Animal Cell Section 7-2 Cytoplasm Nucleolus Nucleus Ribosomes Cell Membrane Mitochondria Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Golgi Bodies Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Eukaryotic Cell Organelles and Function Mitochondria 6. Nickname: “The Powerhouse” Function: Energy formation Breaks down food to make ATP ATP: is the major fuel for all cell activities that require energy Eukaryotic Cell Organelles and Function Vacuoles 7. Function: stores water This is what makes lettuce crisp When there is no water, the plant wilts Intro to the Plant Cell Figure 7-5 Plant and Animal Cells Section 7-2 Plant Cell Vacuole Cell Membrane Go to Section: Evaluate: Animal Cell Drawing Students will draw the animal cell and label each organelle of the cell. You can find this drawing on page 22 E in your Science book H.w. Pg Now let’s talk about structures only found in PLANT Cells!! Figure 7-5 Plant and Animal Cells Plant Cell Section 7-2 Vacuole Chloroplasts Cell Membrane Go to Section: Eukaryotic Cell Organelles and Function Chloroplasts 8. Function: traps energy from the sun to produce food for the plant cell Green in color because of chlorophyll, which is a green pigment Chloroplasts Figure 7-5 Plant and Animal Cells Plant Cell Section 7-2 Vacuole Chloroplasts Cell Membrane Cell Wall Go to Section: Eukaryotic Cell Organelles and Function Cell Wall 9. Function: provides support and protection to the cell membrane Found outside the cell membrane in plant cells Plant Cell Cytoplasm Vacuole Smooth ER Ribosomes Chloroplasts Cell Membrane Cell Wall Nucleolus Golgi Bodies Nucleus Mitochondria Rough ER Comparing Plant and Animal Cells Plant Animal