* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What type of cells did you observe?
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
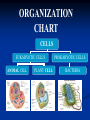
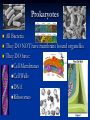
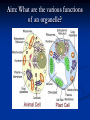
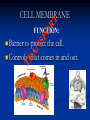
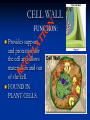
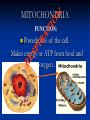
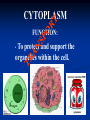
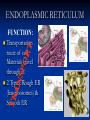
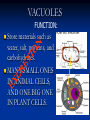
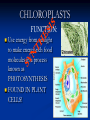
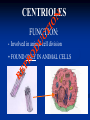
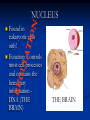
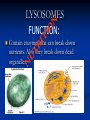
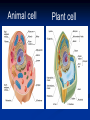
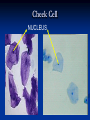
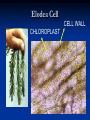
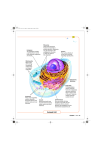
Aim: How can we describe the structure and function of cell organelles? ORGANIZATION CHART CELLS EUKARYOTIC CELLS ANIMAL CELL PLANT CELL PROKARYOTIC CELLS BACTERIA Prokaryotes All Bacteria They DO NOT have membrane bound organelles. They DO have: Cell Membranes Cell Walls DNA Ribosomes 2 Types of Eukaryotic Cells: Animal Cell Plant Cell Both are complex, but there are differences What are those things inside the cell? Organelles- Specialized structures in cells that perform important cellular functions. Life Functions Nutrition – to take in food Transport – to move materials Cell respiration – Make Energy: ATP Excretion – to get rid of waste Synthesis – to build, to make Regulation – to control Growth – to increase in size Reproduction – to make offspring Do Now Define: Homeostasis Cellular Respiration Aim: What are the various functions of an organelle? CELL MEMBRANE FUNCTION: Barrier to protect the cell. Controls what comes in and out. CELL WALL FUNCTION: Provides support and protection for the cell and allows materials in and out of the cell. FOUND IN PLANT CELLS. MITOCHONDRIA FUNCTION: Powerhouse of the cell. Makes energy or ATP from food and oxygen. CYTOPLASM FUNCTION: To protect and support the organelles within the cell. • ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM FUNCTION: Transportation route of cell. Materials travel through it. 2 Types: Rough ER (has ribosomes) & Smooth ER GOLGI APPARATUS FUNCTION: Proteins from ER come here. Labels and packages the proteins, gives them a direction to follow. RIBOSOMES FUNCTION: They FORM proteins Can be found in cytoplasm or on Endoplasmic Reticulum (Rough) VACUOLES FUNCTION: Store materials such as water, salt, proteins, and carbohydrates. MANY SMALL ONES IN ANIMAL CELLS, AND ONE BIG ONE IN PLANT CELLS. CHLOROPLASTS FUNCTION: Use energy from sunlight to make energy-rich food molecules in a process known as PHOTOSYNTHESIS FOUND IN PLANT CELLS! CENTRIOLES FUNCTION: • Involved in animal cell division • FOUND ONLY IN ANIMAL CELLS NUCLEUS Found in eukaryotic cells only! Function: Controls most cell processes and contains the hereditary information DNA (THE BRAIN) THE BRAIN LYSOSOMES FUNCTION: Contain enzymes that can break down nutrients. Also they break down dead organelles. CILIA & FLAGELLA FUNCTION: Made of protein and help with the movement of individual cells Animal cell Plant cell What do plant and animal cells have in common? AMIMAL CELL X X X X X X X X X PLANT CELL Cell Membrane X Cytoplasm X Nucleus X Endoplasmic Reticulum X Ribosome X Mitochondria X Lysosomes X Vacuole X Centriole Chloroplast X Cell Wall X Cheek Cell NUCLEUS Elodea Cell CELL WALL CHLOROPLAST