* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
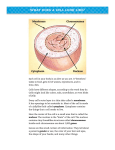
Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function Section 7-1: Life is Cellular Harvard - Inner Life of the Cell The observations and conclusions of many scientists helped to develop the current understanding of the cell Put it in perspective: 1605 – English settlers found the colony at Jamestown, Virginia The Cell Theory Robert Hooke (1665) English physicist used primitive compound microscope to look at plant tissue (cork). He called the chambers “cells” because they reminded him of the small rooms in a monastery The Cell Theory Rudolph Virchow (1855) Proposes that all cells come from existing cells Where did the first cell come from? THE CELL THEORY 1. All living things are composed of cells. 2. Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things. 3. New cells are produced from existing cells. How small are cells? How much is a micrometer? 1 micrometer (µm) = 1/1,000,000 m Typical cell size = 5 to 50 µm in diameter In a dice that is 1 cm3 We could fit 1,000,000 cells Cells Alive How small are cells? Two categories of cells 1. Prokaryotic Cells pro = before; karyon = nucleus or kernel • • contain cell membranes and cytoplasm but no nucleus DNA is scattered through cytoplasm examples: bacteria Two categories of cells 2. Eukaryotic Cells eu = true; karyon = nucleus or kernel contain a nucleus that holds DNA and membrane bound organelles that have specific functions examples: all plants, animals, some fungi, some microorganisms Two categories of cells Prokaryotic -No Nucleus Eukaryotic -Nucleus -Cell wall (plants and -Complex -Less complex bacteria) -Membrane bound -Smaller Ribosomes -Cell membrane organelles less complex -DNA - Ribosomes larger -Cytoplasm and complex -DNA is circular -Ribosomes -DNA is linear Plant Cell - Eukaryotic Prokaryotic Animal Cell - Eukaryotic 7-2 Cell Structures Organelle – a specialized structure that performs a specific function inside a cell Cytoplasm Found – between the nucleus and cell membrane Structure – a clear jelly-like fluid Function – supports the organelles The Nucleus Nuclear Envelope Found: around the outside of the nucleus Structure: two thin membranes with thousands of pores Function: allows materials to move in and out of the nucleus. The Nucleus Chromatin Found: between the nucleolus and the nuclear membrane Structure: DNA bound to proteins Function: contain genetic information The Nucleus Nucleolus Found: In center of the nucleus Structure: a small, dense, round sphere Function: Produces the ribosomes. The Nucleus Found: In the cytoplasm of the cell Structure: a sphere covered by a porous membrane Function: Contains the cell’s DNA and all instruction for making protein and directing cell activities. Nucleolus Chromatin Nucleus Nuclear Envelope Cytoskeleton Found: Throughout the cell Structure: A network of protein filaments Microtubules (25 nm) Microfilaments (7nm) Function: Helps support the cell & maintain shape Involved in several types of movement Cytoskeleton Microfilaments (7nm) Thread like structures made of protein (actin) Support the cell Responsible for cytoplasm streaming – the movement of cytoplasm within a cell (amoeba crawls) Microtubules (25 nm) Tube-like structure made of proteins (tubulins) Important in cell division Used to build cilia and flagella Vacuoles Found: In the cytoplasm Structure: Saclike Very large in plant cells Smaller in animal cells Function: Storage (water proteins, carbs, salts) Vesicles Found: In the cytoplasm Structure: membrane bounded sac Function: transports and/or stores cellular products Lysosomes “The Cells Clean-up Crew” Found: In the cytoplasm Structure: Small enzyme filled organelles Function: Breakdown large organic molecules, and old nonfunctioning organelles Ribosomes Found: In the cytoplasm Structure: Small and grain-like, made of large and small subunits Function: produce proteins from directions given by DNA Endoplasmic Reticulum Found: just outside the nucleus Structure: a maze of membranes Rough ER: (ribosomes imbedded in membrane) produces and transports Smooth ER: (no ribosomes) produces proteins. lipids and detoxifies drugs. Golgi Apparatus Found: In the cytoplasm Structure: A stack of membranes Function: to modify, sort and package materials from the ER for storage or to be transported outside the cell. Chloroplast Found: In the cytoplasm of plant cells Structure: Stack of membranes that contain photosynthetic pigments (chlorophyll) Function: Use energy from the sun to make food (photosynthesis) Mitochondria “Powerhouse of the Cell” Found: In the cytoplasm Structure: Rod-shaped with a folded double membrane Function: Provide the cell with energy. Cell Wall Found: Located outside the cell membrane Structure: Fibers of carbohydrate, cellulose in plant cells Function: Provide support and protection for the cell Cell Membrane Found: Located around the perimeter of the cell Structure: Made of a phospholipid bilayer Function: Regulates what leaves and enters the cell and provides protection and support Centrioles Found: Within the cytoplasm only in animal cells Structure: Made of a microtubules (tubulin) Function: Help organize the cell during cell division. Centrioles - Miosis