* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Looking Inside Cells
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
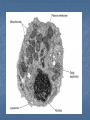
Looking Inside Cells Create a chart with four columns: Name Description Function Drawing Cell Wall Description: Rigid, nonliving, made of cellulose, surrounds plant cells. Function: Protects and supports the cell. Cell Membrane Description: Thin, flexible, has pores. Function: Semipermeable, controls what substances enter and leave the cell. “Gate-keeper.” Cytoplasm Description: Clear, thick, gel-like fluid. Function: Supports all the organelles (tiny cell structures.) Nucleus Description: Large, oval, surrounded by a nuclear membrane with pores. Function: Directs all cell activities. “Brain.” Chromatin/Chromosomes Description: Strands of DNA inside the nucleus Function: Is the genetic material that are the instructions to direct the cell. Nucleolus Description: Round object inside the nucleus. Function: Makes ribosomes. Mitochondria Description: Rodshaped, has a double membrane. Function: Produce energy. “Powerhouse.” Endoplasmic Reticulum Description: Maze of passageways. Some have ribosomes stuck on the outside, some do not. Function: Carry proteins and other materials to different parts of the cell. “Hallways.” Ribosomes Description: Small, round, grain-like. Can be found in cytoplasm or attached to the ER. Function: Produce proteins. Golgi Bodies Description: Flattened stack of sacs. Function: Receive, package, and distribute proteins. “Mail room.” Chloroplasts Description: Rodshaped, green. Function: Produce sugar for plants. “Cafeteria.” Vacuoles Description: Water-filled sacs. Function: Store water, food, wastes. Lysosomes Description: Small, round, contain digestive chemicals. Function: Break down large food particles into small ones, digest old cell parts. “Clean-up crew.” http://www.phschool.com/atschool/science_activ ity_library/plant_animal_cells.htmlhttp://www.lif e.uiuc.edu/cgi-bin/plantbio/cell/cell.cgi http://www.acceleratingfuture.com/peopleblog/?p=147