* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Structure - Brooklyn High School
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
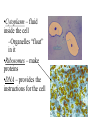
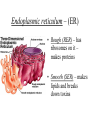
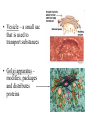
Cell Structure Microscopes Light • Uses a beam of light • Can magnify up to 2000x • Can observe living specimens Electron • Uses a beam of electrons • Can magnify up to 500,000x • Can only observe dead specimens • TEM – looks through a thin layer of tissue • SEM – Used to observe external features Cell Theory • All living things are made of one or more cells • Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living organisms • All cells arise from existing cells * Memorize this * Formation of the Cell Theory • Van Leeuenhoek – created the microscope and used it to see “animalcules” in pond water • Hooke – looked at bark and saw empty boxes he named “cells” • Schleiden – looked at plants and determined they were all made of cells • Schwann – looked at animals and determined they were all made of cells • Remak, Virchow, Redi – biogenesis – “life comes from life” Pasture – finally “proved” the theory of biogenesis Features of all cells • Cell Membrane – made of phospholipids – Polar head and non polar tail – Selectively permeable – only some things pass through – Fluid –Mosaic model •Cytoplasm – fluid inside the cell –Organelles “float” in it •Ribosomes – make proteins •DNA – provides the instructions for the cell Prokaryotic Cells • Do not have membrane bound structures inside of them • Cell wall – a rigid outer structure that helps give shape and provide protection. • The DNA is a single loop – NOT in a nucleus! • Flagella – a hair-like projection used for movement • Smaller than eukaryotic cells Many Bacteria Live in Extreme Environments • • • • Halophiles Thermophiles Aerobic Anaerobic – Facultative anaerobes – Obligate Anaerobes Eukaryotic Cells (Plant and Animal Cells) • Cells have a nucleus – Nucleus is where the DNA is located – Surrounded by a nuclear envelope • Membrane-bound organelles – Organelles are structures that carry out specific jobs in the cell • May use cilia or flagella for movement or to move substances across the cell surface – Cilia are little hairs • Cytoskeleton – supports the shape of the cell, helps transport organelles and substances – Microtubules • Thin, hollow • Made of proteins – Microfilaments • Smaller than microtubules • Solid • Centrioles – help move chromosomes during cell division – Made of microtubules – Found in animals Endoplasmic reticulum – (ER) • Rough (RER) – has ribosomes on it – makes proteins • Smooth (SER) – makes lipids and breaks down toxins • Vesicle – a small sac that is used to transport substances • Golgi apparatus – modifies, packages and distributes proteins • Lysosomes – small sacs that contain digestive enzymes • Mitochondria – the cell’s power plant – Endosymbiotic theory – A prokaryote began to live in a larger cell as the result of a symbiotic relationship. • Has a double membrane • Has DNA – circular like prokaryotes • Reproduces independently of the cell Plant Cells • Cell wall – made of cellulose • Chloroplasts – site of photosynthesis – Also thought to be endosymbionts – DNA is very similar a photosynthetic bacteria • Central Vacuole – takes up most of the plant cell – contains water, food, and wastes – When the vacuole is full, the plant stands upright – When it is not full the plant wilts and droops