* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
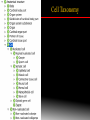
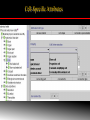
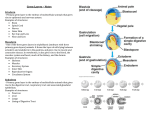
Cell Ontology Workshop 2010 (Bar Harbor, May 18-19, 2010) The Foundational Model of Anatomy (FMA) Ontology: Framework for Cell Classification Onard Mejino Structural Informatics Group Department of Biological Structure University of Washington Anatomical Structures Lung Thorax Cell Heart Macromolecule Background 1838: Theory of Cell by Schleiden and Schwan 1. All living things are made up of cells. 2. Cells are the smallest units of living things 3. Cells only rise from existing cells by division. Modern tenets added: 4. Cells contains hereditary information which is passed from cell to cell during cell division 5. All cells are basically the same in chemical composition. 6. All energy flow (metabolism & biochemistry) of life occurs within cells Background 1838: Theory of Cell by Schleiden and Schwan Cell classification - informatics organize and integrate data - based on traditional contemporary hard copy sources inadequate and inconsistent - requires ontology human readable machine-processible Problem What is a cell? Definition Problem What is a cell? Definition The cell is the functional basic unit of life. Problem What is a cell? Definition The cell is the functional basic unit of life. the smallest living unit capable of independent function, consisting of cytoplasm containing various subcellular compartments (organelles and cytosol and separated from the external environment by the plasma membrane. Problem What is a cell? Definition -based on structure Generalia Differentia Problem What is a cell? Definition Generalia wall compartment (Latin cella) Differentia Generic cell Specialized cell Muscle fiber Neuron Problem How are cells classified? From available sources, we can identify at least ten different ways to classify cells: •Cell shape (squamous, cuboidal, columnar) •Tissue type (muscle, nervous tissue, epithelium) •Nucleated, non-nucleated •Somatic, germ •Colligocyte (fixed), Solocyte (free) •Differentiated, precursor •Lobocyte/filocyte, •Vibriocyte/non-vibriocyte •Embryonic lineage (endoderm, mesoderm, ectoderm) •Secretory, non-secretory •Proliferating, non-proliferating Cell Taxonomy Cell Taxonomy • • • • • Presence of nucleus Somatic, germ Tissue type Embryonic derivation Free, fixed Cell Taxonomy • Presence of nucleus • Somatic, germ • Tissue type • Embryonic derivation • Free, fixed • • • • Proliferative stage Structural properties Lobocyte or filocyte Vibriocyte or nonvibrio-cyte Secretory, non-secretory Membrane markers/surface antigens Cell-Specific Attributes Cell-Specific Attributes Cell-Specific Attributes Cell types ~ 750 human cell types (August Agoncillo) - 300 from UMLS and Cell Ontology Pre-coordination Post-coordination myoepithelial cell (CL) of intralobular lactiferous duct (FMA)