* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download A Tour of the Cell - Ludlow Independent Schools
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Microtubule wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
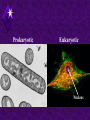
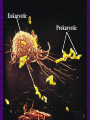
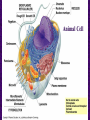
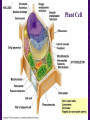
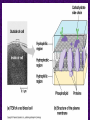
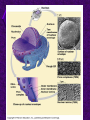
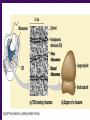
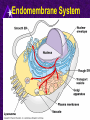
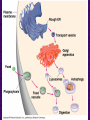
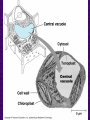
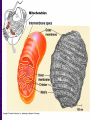
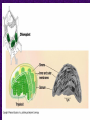
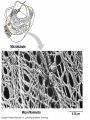
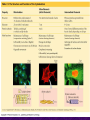
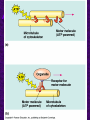
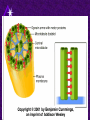
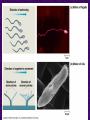
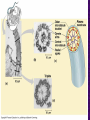
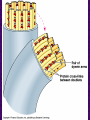
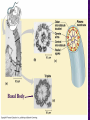
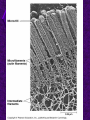
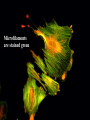
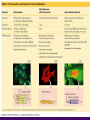
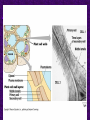
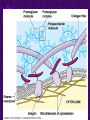
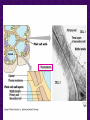
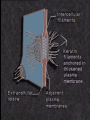
Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell “Faith is a fine invention when gentlemen can see, but microscopes are prudent in an emergency.” Emily Dickinson Question ? Can cells be seen with the naked eye? Light Microscope - LM Light Microscope Occular Lens Objective Lens Stage with specimen Light Source Magnification Resolution Limitations - LM Electron Microscopes TEM SEM Advantages Disadvantages Transmission Electron Microscope - TEM TEM Limitations Scanning Electron Microscope - SEM Excellent views of surfaces. Produces 3-D views. Live specimens possible. Limitations Lower magnifications than the TEM. Cell Biology or Cytology Cyto = cell - ology = study of Should use observations from several types of microscopes to make a total picture of how a cell is put together. Other Tools for Cytology Cell Fractionation Cell Fractionation Chromatography Electrophoresis History of Cells History of Cells 1833 - Robert Brown, discovered the nucleus. 1838 - M.J. Schleiden, all plants are made of cells. 1839 - T. Schwann, all animals are made of cells. 1840 - J.E. Purkinje, coined the term “protoplasm”. Cell Theory R. Virchow Types of Cells Prokaryotic Eukaryotic – -. Both Have: Prokaryotic Eukaryotic Nucleus Eukaryotic Prokaryotic Why Are Cells So Small? Basic Cell Organization Animal Cell Plant Cell Membrane Cytoplasm or Cytosol Organelle Organelles - function You must be able to: Nucleus Structure Nuclear Membrane Nuclear Pores Nucleolus Chromatin Chrom: colored - tin: threads Nucleus - Function Ribosomes Subunits Locations Free in the cytoplasm -. Membrane bound - Endomembrane System Endomembrane System Endoplasmic Reticulum Structure of ER Types of ER Smooth Rough ER: ER: Golgi Apparatus Structure Has 2 Faces Cis face – Trans face - Function of Golgi Bodies Golgi Vesicles Lysosome Function Lysosomes Vacuoles Protists Plants Function Function: Plant vacuole Microbodies Peroxisomes: Glyoxysomes: Enzymes in a crystal Mitochondria . Inner Membrane Function Mitochondria Chloroplasts Inner or Thylakoid Membranes Function Chloroplasts Plastids Examples Amyloplasts/ Leucoplasts – Chromoplasts - Ergastic Materials Cytoskeleton Functions Components Microtubules Hollow Tubulin Intermed. Microfilament Filaments Solid Cables Actin (Keratin) Dynein Cilia/Flagella Muscle Contraction Cell Division Anchors Organelles Microtubules Tubulin . Microtubules Microtubules Cilia and Flagella Cilia and Flagella Dynein Protein Centrioles Basal Bodies Basal Body MTOCs Microfilaments Microfilaments are stained green. Functions Intermediate Filaments Functions Cytoskeleton Cell Wall Plant Cell Walls Primary Wall Secondary Wall Middle Lamella Cell Walls . Extracellular Matrix ECM Intercellular Juctions Plasmodesmata Intercellular Juctions Tight Junctions Desmosomes Gap Junctions Summary Answer: Why is Life cellular and what are the factors that affect cell size? Be able to identify cellular parts, their structure, and their functions.