* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1 - Edutainment
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
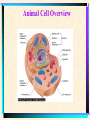
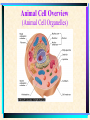
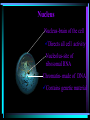
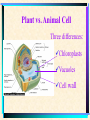
The Microscopic World of Cells Cell membranes Cell Plant vs. animal and transport Organelles cell TYPES of CELLS • Prokaryotic Cells • Prokaryotes are very simple cells, probably first to inhabit the earth. Prokaryotic cells do not contain a membrane bound nucleus. Bacteria are prokaryotes. DNA of bacteria is circular. • The word "prokaryote" means "before the nucleus" • Other features found in some bacteria: • Flagella - used for movement Pilus - small hairlike structures used for attaching to other cells Capsule - tough outer layer that protects bacteria, often associated with harmful bacteria • Eukaryotic Cells • Eukaryotic cells are more advanced cells. These cells are found in plants, animals, and protists (small unicellular "animalcules"). • The eukaryotic cell is composed of 4 main parts: • cell membrane - outer boundary of the cell • cytoplasm - jelly-like fluid interior of the cell • nucleus - the "control center" of the cell, contains the cell's DNA (chromosomes) • organelles - "little organs" that carry out cell functions Animal Cell Overview Cell Membrane and Transport Composed of phospholipids Arranged in a bilayer •marker proteins •receptor proteins Active transport Passive transport •osmosis •diffusion Animal Cell Overview (Animal Cell Organelles) Nucleus Nucleus-brain of the cell Directs all cell activity Nucleolus-site of ribosomal RNA Chromatin- made of DNA Contains genetic material Mitochondria I need more power!! Supplies the cells energy- power plant of the cell Endoplasmic Recticulum Series of flattened membranous sacs. Acts like the cells freeway, transportation system. Ribosomes Site of protein synthesis. Often found lining the E.R. May be found floating free in cytoplasm. Golgi Complex A series of flattened sacs Acts like a mailman, packages and sorts proteins for delivery throughout the cell Centrioles A group of microtubules that aid in cell division. Lysosome Plant vs. Animal Cell Three differences: Chloroplasts Vacuoles Cell wall Chloroplast Site of 6CO2+6H20 C6H12O6+6O2 Do not exist in animal cells, give plant cells their rigidity. Exists in animals but is much larger in plants. Used to store food, waste, gases, pigments, water. Cell Quiz 1. Name 3 differences between plant and animal cells. 2. What organelle is the site of protein synthesis? 3. What organelle acts like the post office? 4. What organelle aids in cell division? 5. How does water enter the cell? Bibliography Integrated Biology/Chemistry A, Continuity of Life Notebook, CORD,Waco, Texas, 1994. www.dcn.davis.ca.us/~carl/cellhome.htm Microsoft Encarta Reference Suite 99, 19931998. http://biodidac.bio.uottawa.ca/Thumbnails/sear chresults.htm The End!