* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 79099_Mitosis
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Kinetochore wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Spindle checkpoint wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
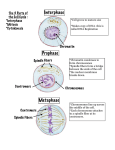
Stages of Mitosis What’s happening and where are things moving to? Interphase Represents the longest time period of the cell cycle Busiest phase of the cell cycle G1: Cell grows in size and protein production is high S: Cell copies it’s chromosomes G2: After DNA is replicated organelles such as mitochondria are manufactured and cell parts needed for cell division are assembled. Prophase - Formation of sister chromatids • • • • • • • Chromatin coils up and chromosomes become visible. Formation of sister chromatids held together by the centromere. Nucleus begins to disappear Nucleolus disintegrates. Centrioles begin to move to opposite ends of the cell. ( animal cells) Spindle begins to form - made from thin fibers of microtubules. In plant cells, spindle forms without centrioles. Metaphase - aligning into the middle Shortest phase of mitosis Double chromosomes ( sister chromatids ) become attached to spindle fibers by their centromeres. Chromosomes pulled by spindle fibers to the middle of the cell. Each sister chromatid is attached by it’s spindle fiber that extends to the oppoosite pole. Anaphase - Separation of sister chromatids Centromeres split apart. Chromatid pairs separate from each other. Pulled apart by the shortening of the microtubules in the spindle fibers. Telophase Begins when chromatids reach the opposite poles. Spindle breaks down Nucleolus reappears New nuclear envelope forms around each set of chromosomes. Lastly, a new double membrane forms between two new nuclei. This is called cytokinesis. Cytokinesis – cell division Final stage of cell reproduction Division of the cytoplasm into approximately equal halves, resulting in a roughly equal distribution of organelles in each of the daughter cells. In cells lacking a cell wall occurs through a pinching inward Organisms with a cell wall undergo a process through which a so-called cell plate is built from the middle of the cell outward to the membrane.