* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Grade 8 review
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
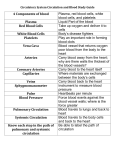
Grade 8 Review Cells to Systems Cell Parts • Q1: What is the function of the mitochondria? Cell Parts • A1: the function of the mitochondria is to create energy for the cell. Cell Parts • Q2: What is the function of the nucleus? Cell Parts • A2: The nucleus is the control centre of the cell. Cell Parts • Q3: What two extra organelles are found in plants only? Cell Parts • A3: Chloroplasts and Cell Wall Cell Parts • Q4: What is the function of the chloroplast? Cell Parts • A4: The function of the chloroplast is to create food from light – PHOTOSYNTESIS. Cell Parts • Q5: What is the function of the cell membrane? Cell Parts • A5: - controls the movement of substances in and out. - Provides protection (keeps foreign bodies out) - Holds the cell together - shape Cell Parts • Q6: What is the following organelle? Cell Parts • A6: Golgi Apparatus Circulation • Q7: What prevents blood from moving backwards in the heart and veins? Circulation • A7: Valves Circulation • Q8: What is the largest artery in the body? Circulation • A8: The Aorta Circulation • Q9: What molecule in the blood makes the blood red when combined with oxygen? Circulation • A9: Hemoglobin. Circulation • Q10: What are 2 waste products of respiration? Circulation • A10: Water and Carbon Dioxide Circulation • Q11: Approximately how many times does an average person’s heart beat while resting? Circulation • A11: 70-75 bpm Circulation • Q12: What is the large vein from the top of the body that enters the right atrium called? Circulation • A12: Superior Vena Cava. Microscopy • Q13: What part of the compound light microscope controls the amount of light that enters the microscope? Microscopy • A13: The diaphragm Microscopy • Q14: Who invented the microscope around the year 1609? Microscopy • A14: Anton von Leeuwenhoek Microscopy • Q15: If the ocular lens is 10x and the objective lens is 20x, what is the overall magnification? Microscopy • A15: 10 x 20 x = 200x Microscopy • Q16: How have microscopes advanced science and medicine? Microscopy • A16: - showed us “invisible” organisms - Helped us learn about cells and their function - Taught us about disease Cell Organization • Q17: What is a group of similar cells working together called? Cell Organization • A17: Tissues Cell Organization • Q18: What is a group of organs working together called? Cell Organization • A18: Organ Systems? Cell Organization • Q19: What organ system is made of - alveoli, pharynx, larynx and sinuses? Cell Organization • A19: Respiratory System Cell Organization • Q20: What organ system is made of - Thrombocytes - Erythrocytes - Myocardial tissues Cell Organization • A20: The Circulatory System