* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cells Alive – Internet Lesson Part A. “HOW BIG IS A …”
Survey
Document related concepts
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
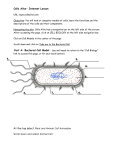
Cells Alive – Internet Lesson URL: www.cellsalive.com Objective: You will look at computer models of cells; learn the functions and the descriptions of the cells and their components. Navigating the site: Cells alive has a navigation bar at the left. After accessing the page, click on CELL BIOLOGY on the left side navigation bar. From here, you will access the links: “How Big is a…” the animal cell model, the plant cell model, and the bacterial cell mode. Part A. “HOW BIG IS A …” Here you will look at objects found on the head of a pin. Your job is to estimate the length of each (in nanometers, micrometers, or millimeters). The line in the bottom right corner of the screen is used to help you estimate. Sketch each of the objects in the first column, and estimate the size in the second column. OBJECT Human hair Dust mite Pollen grain Lymphocyte Red blood cell Bakers yeast E. coli Staphylococcus Ebola virus Rhinovirus SKETCH SIZE (nanometers, micrometers, or millimeters) Part B: Bacterial Cell Model You will need to return to the “Cell Biology” link to access this page, or hit your back button. Label the bacterial cell below. Part C: Animal Cell Model You will need to return to the “Cell Biology” link to access this page, or hit your back button. Sketch the following organelles of the animal cell and answer the following questions. For this model, you will need to click on the various parts of the cell to go to a screen that tells you about the parts. MITOCHONDRIA Sketch the organelles below. 1. What do mitochondria do? 2. How big are mitochondria? 3. What kind of cells contains the most mitochondria? Mitochondria LYSOSOME 4. What is the function of a lysosome? Lysosome 5. What is found within the lysosome that performs the function in the previous question? GOLGI APPARAUS Golgi apparatus 6. What does the Golgi apparatus do? 7. Is the Golgi apparatus a membrane bound organelle? Is this structure found in prokaryotes? ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM Rough ER Smooth ER 8. What is the difference between rough and smooth ER? 9. Rough ER is associated with making what product? 10.Smooth ER is involved in what functions? NUCLEUS 11.What is found in the nucleus that controls cellular activities? 12.During cell division, chromatin is transformed into what structure? Nucleus NUCLEOLUS Nucleolus 13.Where is the nucleolus found? 14.What does the nucleolus do? RIBOSOME Ribosome 15.What is the function of the ribosome? CENTRIOLES 16.What is the function of the centrioles? centrioles 17.What is a pair of centrioles? 18.Centrioles play a major role during what process? MICROTUBULES AND MICROFILAMENTS 19.Together, the microtubules and filaments form what structure? 20.Two functions of the microtubules and filaments are: microtubules microfilaments PLASMA MEMBRANE cell membrane 21.What composes the plasma membrane? 22.How many layers is the plasma layer? 23.What is embedded within the membrane that acts as receptors and gateways for other substances to pass? Part D: Plant Cell Model You will need to return to the “Cell Biology” link to access this page, or hit your back button) 1. What other type of cell has a cell wall? 2. What makes the plant cells green? 3. In plant cells, what does the vacuole do? 4. What is the cell wall composed of in most plants? Sketch the following organelles. chloroplast vacuole cell wall