* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Vestibulospinal Tract - Viktor`s Notes for the Neurosurgery Resident
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Eyeblink conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Pre-Bötzinger complex wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
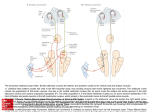
VESTIBULOSPINAL TRACT A50 (2c) (1) Vestibulospinal Tract Last updated: April 30, 2017 Involved in the maintenance of extensor tone Fibers from lateral vestibular nucleus travel ipsilaterally within the entire length of the cord in the anterior part of the lateral funiculus laminas VII, VIII, and IX and directly to the α and gamma motor neurons and interneurons, with somatotopic organization. Stimulation causes extension The vestibulospinal tract arises from the lateral vestibular nucleus (Deiters nucleus) and descends ipsilaterally in the lateral funiculus of the spinal cord. Vestibulospinal neurons synapse in laminae VII, VIII, and IX of the spinal cord. Several vestibulospinal fibers synapse directly with α and ϒ motor neurons of the ventral horn. The vestibulospinal tracts facilitate extensor muscle group tone. Lesions of the brainstem between the inferior and superior colliculi (above the vestibular nuclei and below the red nuclei) result in extensor (decerebrate) posturing of the upper and lower extremities. This results from the loss of lateral vestibular nuclei inhibition from higher brain centers. VESTIBULOSPINAL TRACT BIBLIOGRAPHY for ch. “Spinal Cord” → follow this LINK >> A50 (2c) (2) Viktor’s Notes℠ for the Neurosurgery Resident Please visit website at www.NeurosurgeryResident.net