* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Membranes, Transport and Macromolecules TEST 2 KEY
Survey
Document related concepts
Model lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
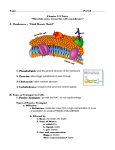
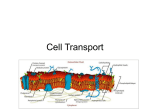
Name: _________________________________________________________Period: ______ Alpha#: ______ Unit 2: Molecules and Membranes (1pt each) Multiple Choice: Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A reaction that removes water as it combines 2 monomers into a polymer is called A. dehydration synthesis B. hydrolysis C. combustion D. decomposition 2. The macromolecules used in for enzymes and structure in your cells and body are A. carbohydrates B. lipids C. proteins D. nucleic acids 3. The macromolecules that carry the genetic information or synthesize proteins are: A. carbohydrates B. lipids C. proteins D. nucleic acids 4. Monosaccharides are the monomers that make a: A. carbohydrate B. protein C. lipid D. nucleic acid 5. Cell walls are made of this polysaccharide: A. starch B. glucose C. cellulose D. glycogen 6. Amino acids are the monomers that make a: A. carbohydrate B. protein C. lipid D. nucleic acid 7. This lipid is the primary component of cell membranes A. Fat B. oil C. cellulose D. phospholipid 8. Which carbohydrate is produced by photosynthesis? A. glycogen B. glucose C. cellulose D. starch 9. The passive transport of water across a selectively permeable membrane is called A. dynamic equilibrium. B. facilitated diffusion. C. osmosis. D. active transport 10. Nucleotides are the monomers that make a: A. carbohydrate B. protein C. lipid D. nucleic acid 11. A Glycerol monomer and 3 fatty acids (triglycerides) make: A. carbohydrate B. protein C. lipid D. nucleic acid 12. A reaction that adds water as it breaks a polymer into its monomers is called: A. dehydration synthesis B. hydrolysis C. combustion D. decomposition 13. The macromolecules used for insulation, structure, and long-term energy storage are: A. carbohydrates B. lipids C. proteins D. nucleic acids 14. The macromolecules used in the cell for short term energy and structure are: A. carbohydrates B. lipids C. proteins D. nucleic acids 15. The part of the cell that maintains homeostasis by regulating what enters and leaves the cell is the A. cell wall B. nuclear membrane C. cell membrane D. cytoplasm 16. Large molecules that cannot fit through the cell membrane are brought into the cell by A. endocytosis B. exocytosis C. facilitated diffusion D. osmosis 17. When a cell maintains stable internal conditions this is called A. active transport B. equilibrium C. homeostasis D. passive transport 18. Which of the following are all types of active transport? A. osmosis, endocytosis, exocytosis C. diffusion, osmosis, facilitated diffusion B. exocytosis, endocytosis, active transport D. osmosis, active transport, facilitated diffusion 19. What makes active transport different from passive? A. Uses ATP and goes with the concentration gradient B. Uses ATP and goes against the concentration gradient C. Does not use ATP and goes with the concentration gradient D. Does not use ATP and goes against the concentration gradient 20. Choose the solution that will be hypertonic to a cell that has 30% solute, 70% water. A. 20% solute, 80% water C. 45% solute, 55 % water B. 30% solute, 70% water D. 10% solute, 90% water 21. Choose the solution that will be hypotonic to a cell that has 30% solute, 70% water. A. 50% solute, 50% water C. 45% solute, 55 % water B. 60% solute, 40% water D. 10% solute, 90% water 22. More water moves into a cell than out of it when the cell is placed in a solution….. A. with a higher concentration of salts to the cell B. with an equal concentration of salts to the cell C. with a lower concentration of salts to the cell D. none of the above 23. Phospholipid molecules are well suited to forming cell membranes because they: A. form a solid barrier of protein. B. allow some substances to enter the cell and keeps others out. C. dissolve in water. D. allow all substances to pass through the membrane. 24. When a sea urchin egg is removed from the ocean and placed in freshwater, the egg swells and bursts. Which of these causes water to enter the egg? A. Diffusion B. Sodium pump C. Active transport D. Osmosis 25. Which of these best explains why a freshwater aquarium would be a dangerous habitat for saltwater fish? A. The cells of the saltwater fish would gain too much water. B. The organs of the saltwater fish would produce too much protein. C. The organ systems of the saltwater fish would consume too much energy. D. The tissues of the saltwater fish would absorb too much acid. 26. Which of these is a function of the cell membrane in all cells? A. Producing cellular nutrients B. Preserving cellular wastes C. Neutralizing chemicals D. Maintaining homeostasis 27. Which statement regarding the functioning of the cell membrane of all organisms is NOT correct? A. The cell membrane forms a boundary that separates the cellular contents from the outside environment. B. The cell membrane is capable of receiving and recognizing chemical signals. C. The cell membrane forms a barrier that keeps all substances that might harm the cell from entering. D. The cell membrane controls the movement of molecules into and out of the cell. 28. The diagram below represents movement of a large molecule across a membrane. Which process is best represented in this diagram? A. active transport B. diffusion C. protein building D. gene manipulation 29. In the diagram below, the dark dots indicate small molecules. These molecules are moving out of the cells, as indicated by the arrows. The number of dots inside and outside of the two cells represents the relative concentrations of the molecules inside and outside of the cells. ATP is being used to move the molecules out of the cell by: A. Cell A C. both cell A and cell B B. Cell B D. neither cell A nor cell B 30. The diagram below represents a cell in water. Formulas of molecules that can move freely across the cell membrane are shown. Some molecules are located inside the cell and others are in the water outside the cell. Based on the distribution of these molecules, what would most likely happen after a period of time? A. The concentration of O2 will increase inside the cell. B. The concentration of CO2 will remain the same inside the cell. C. The concentration of O2 will remain the same outside the cell. D. The concentration of CO2 will decrease outside the cell. 31. What usually results when an organism FAILS to maintain homeostasis? A. Growth rates within organs become equal. B. The organism becomes ill or may die. C. A constant sugar supply for the cells is produced. D. The water balance in the tissues of the organism stabilizes. 32. Diffusion is the movement of molecules from ____________. A. an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration B. an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration C. an area at equilibrium to an area of high concentration D. an area of low concentration to an area at equilibrium 33. Which type of transport requires a cell to use energy (ATP)? A. Facilitated diffusion B. Diffusion C. Active transport D. Passive transport 34. Cholesterol molecules are spaced between the phospholipids in the cell membrane to A. identify the cell to the immune system C. receive signals from outside the cell B. keep the membrane fluid D. allow materials into the cell The following diagram is a cross section of a cell membrane. Match the structures listed with the correct letter. A. 35. transport protein C 36. phospholipid bilayer D C 37. hydrophobic part of P-lipid bilayer E .. 38. hydrophilic part of P-lipid bilayer B C ..C. D. 39. glycoprotein A E 40. This polysaccharide makes up the exoskeletons of insects and crustaceans A. glycogen B. starch C. chitin D. cellulose 41. Fats and oils are A. carbohydrate C. lipid B. protein B. D. nucleic acid 42. DNA DOES NOT have which of the following characteristics A. double stranded C. A,G,C, and T nucleotides B. used as genetic material D. ribose sugar in its nucleotides 43. What kind of carbohydrate is the sugar in milk (lactose)? A. monosaccharide C. polysaccharide B. disaccharide D. simple sugar 44. RNA DOES NOT have which of the following characteristics A. single stranded C. A,G,C, and U nucleotides B. used as genetic material D. ribose sugar in its nucleotides 45. The cell membrane is selectively permeable. This means that A. it allows all molecules in/out of the cell B. it allows only certain molecules in/out of the cell C. it allows no molecules in/out of the cell D. it only allows molecules to leave the cell 46. In facilitated diffusion, molecules A. move directly through the phospholipid bilayer, from a high to low concentration B. move directly through the phospholipid bilayer, from a low to high concentration C. move from a high to low concentration, through a transport protein. D. move from a low to a high concentration, through a transport protein. 47. A beaker is filled with a salt solution (40% salt and 60% water). The bag is also filled with a salt solution (50% salt and 50% water). The bag is impermeable to salt so the salt molecules cannot cross. How will the molecules behave in this situation? A. The water will diffuse out of the bag and the salt will diffuse in B. The water will diffuse into the bag and the salt will not move. C. The water will diffuse out of the bag and the salt will not move D. The water will diffuse into the bag and the salt will diffuse out Short Answer: 48. (2pts) Name the four types of biological macromolecules: A. Carbs C. Proteins B. Lipids D. Nucleic Acids 49. (6pts) Three rectangular shaped cells were placed in the following solutions. A. Write below each drawing whether the solution is hypotonic, hypertonic or isotonic to the cell. Then draw and label an arrow in the direction of water movement (osmosis) between the cell and the solution. B. Diffusion can occur at the same time as osmosis. Draw and label a different dashed arrow to show the movement of solute between the cell and the solution. A B 10% solute 90% solvent 25% solute 75% solvent 25% solute 75% solvent 5% solute 95% solvent 25% solute 75% solvent 50% solute 50% solvent C A Hypertonic B Hypotonic C Isotonic C. In which solution will the cell expand, shrink, or remain the same? A Shrink B Expand C Remain the same Bonus: (1pt) In a DNA molecule, A bonds with T and C bonds with G (1pt) If a frog (freshwater) egg is placed in the ocean what will happen? The cell will shrink and die (1pt) What color is a positive Benedict’s test? You weren’t to know the answer to this