* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Genetics and Health
Mitochondrial DNA wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
DNA polymerase wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
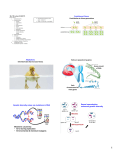
Genetics and Health Jennifer Eyvindson Epi 6181 November 2006 Points to cover Basic Genetics Heredity Replication Translation Mutations Genetics and Health Cancer Genes, behaviour, & social environment Tools to develop Heredity Allele – a particular form of a gene We have 2 copies of each gene Homozygous – 2 copies of same allele Heterozygous – 2 different alleles Dominant (A) vs. Recessive (a) Incomplete Dominance Co-dominance AA Aa aa The basics Chromosomes Condensed DNA Located in Nucleus DNA Blueprint The Double Helix Watson and Crick (1953) 2 Strands of DNA Hydrogen bonds Overview – Genetic processes Replication (DNA DNA) Transcription (DNA RNA) Translation (RNA Protein ) DNA Replication DNA must be copied before every cell division Translation (protein synthesis) 1. Ribosome binds to DNA 2. tRNA binds to mRNARibosome complex and brings Amino Acid 3. Amino Acid chain elongation 4. Protein These Molecular Processes are highly regulated: Promoters Inducers Repressors *Environment Influence Protein Functions Structure & Mechanics Cell Structure Transport Enzymes Catalyze chemical reactions Signalers Hormones Receptors When things go wrong DNA Deletion Insertion Point mutation PROTEIN Non-sense (STOP) Mis-sence Silent It’s not that simple… Human Genome Project (April 2003) map and sequence 3 billion DNA base pairs containing an estimated 30,000 genes 97% Non-coding “JUNK” DNA Polygenetic Inheritance Most traits result from expression of more than one gene Gradients Complex interactions not well understood Genetics and Health Inherited Disorders Allele (Huntington's) X-linked (Hemophilia) Other predispositions Allele variants (Addictions, Depression, Cancer…etc) Errors Cancers Chromosomal abnormalities (Down syndrome) The Genetics of Cancer Tumours are the result of multiple mutations Mutations can be inherited or de novo Genetic Loss Regulatory Apoptosis (Cell self destruct mechanism) DNA repair Genetic Gain Cell Cycle progression Apoptosis inhibitors Genes, Behaviour, and the Social Environment Top Down Social factors influence genetics Environmental mutagens lead to DNA mutations and cancer Environment regulates gene expression Bottom up Genetics influence behaviors, thereby the social environment Inherited traits predispose individuals to act in certain ways Tools to develop Bio Technology Informatics Look at multiple genes, proteins Keep track of 30 000 genes and their interactions Laws and Ethics Genetic profiles ???