* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Year 8 Cell VOCAB
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
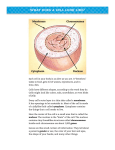
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Single-celled microorganisms, some of which are pathogenic in humans, animals and plants. Singular is bacterium. A selectively permeable membrane surrounding the cell and controlling the entry and exit of materials. Outer structure which provides support and prevents the cell from bursting by the uptake of water by osmosis; plant, fungal and bacterial cell walls have a different structure and chemical composition. Contains the green pigment chlorophyll; the site of photosynthesis. The living substance inside a cell (not including the nucleus). Basic unit of life. Unicellular organisms only have one cell. Multicellular organisms have many cells. Device that uses visible light and a series of lenses to produce an enlarged image of an object. Structures in the cytoplasm of all cells where respiration takes place (singular is mitochondrion). Having more than one cell. The nucleus controls what happens inside the cell. Chromosomes are structures found in the nucleus of most cells. The plural of nucleus is nuclei. A group of different tissues that work together to carry out a particular function, eg heart and lungs. A group of organs that work together to complete a specific function. A cell that has become differentiated to carry out a particular function, eg red blood cell. A group of similar cells that carry out the same function, eg muscle tissue. A single-celled organism. A space within the cytoplasm of plant cells that contains cell sap. EUKARYOTE PROKARYOTE Bacteria Cell cytoplasm cell membrane multicellular organ light microscope cell wall vacuole organ system mitochondria chloroplast tissue unicellular nucleus specialised