* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download RNA, Protein Synthesis, Transcription, and Translation
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
RNA interference wikipedia , lookup
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic transcription wikipedia , lookup
RNA polymerase II holoenzyme wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
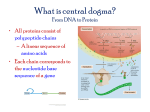
RNA, Protein Synthesis, Transcription, and Translation RNA • Remember, DNA contains instructions that control production of proteins. • These instructions from DNA are copied onto a strand of mRNA. • Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a long chain of nucleotides similar to DNA. Differences between DNA and RNA 1. The sugar in RNA is ribose 2. RNA is single stranded 3. Uracil replaces Thymine in RNA Three Types of RNA 1. Messenger RNA (mRNA) – carry instructions to the rest of the cell 2. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) – found on ribosomes 3. Transfer RNA (tRNA) – transfers amino acid to ribosomes Protein Synthesis • Which organelle is responsible? • Ribosomes. DNA Transcription, Genetic Code, and Translation Transcription • When mRNA is produced. • Part of a DNA nucleotide sequence is copied. • Starts at places called promoter. • Stops when a specific code is given. • Occurs in the nucleus of the cell • Purpose – copy instructions onto mRNA Genetic Code • Amino acids join together to make polypeptides. • Each one contains part or all of the 20 amino acids. • Different proteins determined by which amino acids are joined. Translation • Decoding of instructions found on mRNA is called translation. • Occurs in the cytoplasm, where mRNA attaches to ribosomes. Review • What is the process within a cell in which DNA is duplicated? • REPLICATION • What is the process called when instructions from DNA are copied into mRNA? • TRANSCRIPTION • What are these instructions for? • MAKING PROTEINS Review • What is the process in which these instructions are “decoded”, and proteins begin to be produced? • TRANSLATION • Where in the cell does protein synthesis occur: • CYTOPLASM, ON RIBOSOMES Review • What is the name for three consecutive nucleotides that specify an amino acid? • A CODON • How many amino acids are there? • 20