* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Microtubule wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Spindle checkpoint wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
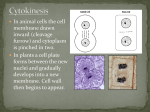
1.6 Cell division Understanding: - Mitosis is division of the nucleus into two genetically identical daughter nuclei - Chromosomes condense by supercoiling during mitosis - Cytokinesis occurs after mitosis and is different in plant and animal cells - Interphase is a very active phase of the cell cycle with many processes occurring in the nucleus and cytoplasm - Cyclins are involved in the control of the cell cycle - Mutagens, oncogenes and metastasis are involved in the development of primary and secondary tumors Applications: - The correlation between smoking and incidence of cancers Nature of science: - Serendipity and scientific discoveries: the discovery of cyclins was accidental Nature of science: - Identification of phases of mitosis in cells viewed with a microscope - Determination of a mitotic index from a micrograph Cell division Mitosis: Division of the nucleus into two genetically identical daughter nuclei Mitosis Needed for: - Embryonic development - Growth - Tissue repair - Asexual reproduction - Four main stages (with one before, and then one after!) - Remember using PMAT Before mitosis… Interphase Very active Numbers of mitochondria in the cytoplasm increase In plant cells the chloroplasts also increase Three phases – G1, S, G2 Interphase Phase G1 S G2 What happens? Before mitosis… Your task Complete the sheet to show the series of events that happen during each stage of mitosis Include diagrams Once you have finished this, make sure you have all notes (check through PPTs so far), then you can revise for your test. Please bring in the following on Tuesday 3rd November Prophase 1. Chromosomes become shorter and fatter by coiling 2. Supercoiling so they become short enough 3. Nuclear membrane breaks down 4. Microtubules start to grow from each pole Prophase Metaphase 1. Chromosomes align on equator of cell 2. Microtubules continue to grow and attach to centromeres on each chromatid 3. Microtubules put under tension to test if they are attached correctly Metaphase Anaphase 1. Each centromere divides 2. Pairs of sister chromatids separate 3. Microtubules pull them towards the poles of the cell Anaphase Telophase 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Chromatids have reached the poles Now called chromosomes Microtubules disappear Chromosomes pulled into a tight group Nuclear membrane forms around them Chromosomes uncoil and decondense and nucleolus formed Telophase After mitosis… Cytokinesis 1. Cell divides into two after telophase Cytokinesis Mitotic Index Ratio between the number of cells in mitosis compared to the total number of cells Number of cells in mitosis Total number of cells MITOSIS DOES NOT INCLUDE INTERPHASE AND CYTOKINESIS How do you tell if the cell is in mitosis? If you can see the chromosomes = in mitosis Calculate the mitotic index Mitotic Index Number of cells in mitosis = Total number of cells MITOSIS DOES NOT INCLUDE INTERPHASE AND CYTOKINESIS Cancer = Higher mitotic index (More cells in mitosis – higher rate of division) Cyclins Discovered by accident by Tim Hunt Control the step by step program of the cell cycle Ensure everything is correct before moving to the next stage Cyclins Bind to enzymes (cyclindependent kinases) Kinases become active and attach phosphate groups to other proteins in the cell Proteins become active Carry out tasks in the cell for specific stage of the cell cycle Four Cyclins Different Cyclins have specific roles and phases Cyclins must reach a threshold before the cell can move to the next stage Controls the cell cycle and ensures the cells do not divide when they are not needed to What if the cell cycle is not controlled properly? Research: - Define the key terms and words - What evidence is there that smoking and cancer are related? Tumor formation and cancer Keyword Benign tumor Definition What is the correlation between smoking and death rate due to cancer? Malignant tumor Carcinogen Mutagen Oncogene Metastasis Correlation What evidence is there for this? Tumor formation and cancer Keyword Benign tumor Definition What is the correlation between smoking and death rate due to cancer? Malignant tumor Carcinogen Mutagen Oncogene Metastasis Correlation What evidence is there for this?