* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Growth and Division
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
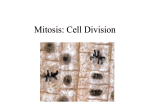
Cell Growth and Division Why Cells Divide 1) DNA overload Small cell – Information stored in DNA meets all the cell’s needs. Huge cell -- Cell growth without limits leads to “_____________ crisis.” The DNA can’t keep up with the cell’s need for proteins. 2) The cell volume becomes too ____________ for the surface area of the cell membrane to manage. Exchange of materials (wastes, nutrients, gases) occurs through the cell membrane. The rate of exchange depends on the surface area of the cell. The rate at which nutrients are used and waste products are produced depends on the ______________ of the cell. Why Cells Divide Ratio of surface area to volume As a cell increases in size, __________ increases much more rapidly than surface area. Ratio of surface area to volume decreases Decrease in ratio causes _________________ for the cell Cell Division To avoid decreasing the ratio of surface area to volume, cells __________________ before they become too large. Each “daughter” cell has a greater ratio of surface area to volume than the “mother” cell. Why Cells Divide Although a giant cell will never threaten a city, cells do come in a wide variety of shapes and sizes. Cell Reproduction Cell ___________—all cells come from pre-existing cells. ____________________ is the process by which new cells are produced from pre-existing cells. Each “daughter” cell gets an ______________ copy of the DNA and half of the cytoplasm and organelles. Cell Reproduction--Prokaryotes In ___________________, cell division takes the form of BINARY FISSION Bacteria have a single, circular DNA molecule with no proteins. First, the DNA is _______________ (replicated) Next, the cell splits into two equal, identical halves. Cell Cycle and Mitosis Genetic information that is passed from one generation to the next is carried by _____________________. Eukaryotic chromosomes are made up of ________ and __________. Cells of every organism have a specific number of chromosomes. Chromosomes are ________ visible in most cells except during cell division. the beginning of cell division, chromatin condenses into chromosomes. Before cell division, each chromosome is _______________. At Each chromosome consists of two identical _______” chromatids attached at a _______________. Chromosomes Replicated chromosome Consists of 2 sister __________________ Exact copies of each other Connected by a _______________ Cell division ____________ chromatids. Each new cell gets one copy of each chromatid. The Cell Cycle Eukaryotes undergo a life cycle known as the ______________________. The Cell Cycle The cell cycle is the series of events that cells go through as they __________ and divide During the cell cycle a cell… Grows Prepares for ________________ Divides to form two daughter cells The Cell Cycle G1 – S – chromosomes are replicated; ____________ is copied G2 – organelles and molecules required for cell division are produced M – mitosis and cytokinesis