* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download cscope Cell Transport And Homeostasis Terms ppt
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
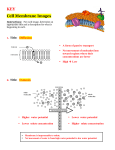
November 7, 2012 (You do not have to write the questions) Cell Transport & Homeostasis Key Terms Biology Unit 04 Lesson 02 Semi-permeable • Allowing certain substances to pass through • Cell membrane is semi-permeable, it allows certain substances to cross but not others Review of the Types of Membranes: 1. 2. 3. Permeable Impermeable Semi-permeable 1. Permeable Write this in your notes! ALL types of molecules can get through, regardless of size or charge. Permeable Pavement 2. Impermeable (non-permeable) Write this in your notes! NO molecules can get through 3. SEMI-PERMEABLE !!!: SOME MOLECULES CAN GET THROUGH – Very small or – Non-charged Write this in your notes! Homeostasis • Regulation of an organism’s internal environment in order to maintain conditions suitable for survival • Happens on the organism and cellular level Passive Transport • Movement of substances across the cell membrane that does not require energy from the cell (high concentration to low concentration) Diffusion • Movement of particles from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration • Type of passive transport Conceptual Diagram: Facilitated Diffusion • Substances cross the cell membrane with the help of special carrier proteins • Type of passive transport Osmosis • Diffusion of water from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration Hypotonic Solution • A solution or environment surrounding a cell that has less dissolved solutes and more water than the cell • This type of solution will cause water to move into the cell via osmosis, resulting in swelling of the cell Hypertonic Solution • A solution or environment surrounding a cell that has more dissolved solutes and less water than the cell • This type of solution will cause water to move out of the cell via osmosis, resulting in shrinking of the cell. Isotonic • A solution or environment surrounding a cell that has the same amount of dissolved solutes and the same amount of water as the cell Active Transport •Movement of particles across a membrane to an area of higher concentration, which requires energy Ion or Protein Pump • Proteins that are able to transport ions across the cell membrane from low to high concentration by changing their shape which requires ATP (energy) from the cell • Example: sodium-potassium pump (important in nerve responses) Endocytosis • Cell brings in a bulky substance from its surroundings by wrapping its membrane around the substance and forming a vesicle • Ex: White blood cells “eat” bacteria using this process. Exocytosis • Cell releases substances by merging a vesicle with the cell membrane and releasing the substances into the fluid around the cell • Ex: cell releases waste products Change in cell membrane (2nd type of active transport process) Endocytosis Takes in (engulfs) large material Cell membrane moves in until it encapsulates material, becoming a vesicle. Endocytosis: (IN) Two types: Phagocytosis Pinocytosis Phagocytosis: “Cell Eating” Pseudopods engulf material with extensions of the cell membrane. Ex. White blood cell taking in foreign material for destruction. Pinocytosis: “Cell Drinking” Membrane wraps around a big drop of solution (solute & solvent) and pulls it in. Pinocytosis: Change in cell membrane (2nd type of active transport process) Endocytosis Takes in (engulfs) large material Cell membrane moves in until it encapsulates material, becoming a vesicle. Exocytosis Vesicle that gets rid of large material Exocytosis: (OUT) Vesicle fuses with cell membrane, releasing contents to outside of cell. ex. Waste ex. Digestive enzymes Exocytosis: (OUT) RNA Rough ER Golgi apparatus Protein in vesicle Plasma membrane Conceptual Diagram: Definitions Solute: – what gets dissolved Solvent: – What does the dissolving, more plentiful that solute Solution: – the mixture of solutes and solvent Example: H2O and NaCl Solute: NaCl Solvent: H2O Solution: H2O and NaCl For each scenario, answer the following questions: Will the H2O move? Will the solute move? Will they reach equilibrium? If equilibrium is reached, what will the solute concentration on each side? For each scenario, answer the following questions: Will the H2O move? Will the solute move? Will they reach equilibrium? If equilibrium is reached, what will the solute concentration on each side?