* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download autonomic nervous system
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroethology wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
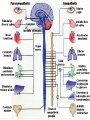
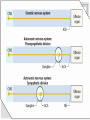
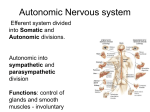
CENTRAL INTEGRATION OF AUTONOMIC FUNCTION KHALED AL-SUHIBANI Advisor : Abd Elmonem Hafez Abd Elmonem OBJECTIVES : • Define Autonomic Nervous system, mention its components and their functions. • Name the neurotransmitters of the autonomic nervous system. WHAT IS AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM ? • It’s the portion of the nervous system that control most visceral function of the body called autonomic nervous system . FUNCTION OF AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM : • This system help to control arterial pressure, gastrointestinal motility, gastrointestinal secretion, urinary bladder emptying, sweating, body temperature, and many other activity. COMPONENT : 1. Sympathetic nervous system 2. Parasympathetic nervous system 1-SYMPATHETIC NERVOUS SYSTEM • The sympathetic nerve fibers originate in spinal cord between cord segment T-1 and L-2 and pass first into the sympathetic chain and then to the tissues and organs that are stimulate by the sympathetic nerves. FUNCTION OF SYMPATHETIC NERVOUS SYSTEM ON SOME ORGANS : 1. Eyes pupillary opening and focusing of the lens. Sympathetic stimulation contracts the radial dilator of the iris pupillary dilation. 2. Heart increase and strength of heart contraction. 3. Gastrointestinal decrease peristalsis and increase the tone of sphincters. 2-PARASYMPATHETIC NERVOUS SYSTEM • The parasympathetic fibers leave the central nervous system through cranial nerves iii, vii, ix and x; and additional parasympathetic fibers leave the lowermost part of the spinal cord through the second and third sacral spinal nerves and occasionally the first and fourth . FUNCTIONS OF PARASYMPATHETIC NERVOUS SYSTEM ON SOME ORGANS : 1. Eyes pupillary opening and focusing of the lens. Parasympathetic stimulation contracts the sphincter muscle of the iris pupillary constriction. 2. Heart decrease the rate of the heart. 3. Gastrointestinal promoting peristalsis and relaxing the sphincter. NEUROTRANSMITTER OF THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM • The sympathetic and parasympathetic nerve fibers secrete mainly one or the other of two synaptic transmitter substances, acetylcholine or norepinephrine. • All preganglionic neurons are cholinergic in both the sympathetic or parasympathetic nervous systems. Therefore, acetylcholine or acetylcholine-like substance, applied to the ganglia, will excite both sympathetic and parasympathetic postganglionic neurons . CONT. • All or almost all of the postganglionic neurons of parasympathetic system are also cholinergic (Acetylcholine). • Most of the postganglionic sympathetic neurons are adrenergic (Norepinephrine). • The postganglionic sympathetic nerve fibers to sweat glands, to the piloerector muscles and to few of blood vessels are cholinergic. CONT. • The hormones in turn act on the different organs to cause the respective parasympathetic and sympathetic effects. • Acetylcholine is called a parasympathetic transmitter. • Norepinephrine is called a sympathetic transmitter. REFRENCESES ANY QUESTIONS ? THANKE YOU