* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Sensory system
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Cortical cooling wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Eyeblink conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Sensory substitution wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Spinal cord wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
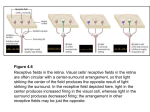
Sensory system Sensory system The sensory system is composed of subsystems, each transmitting specific information to the central nervous system Somatosensory system The somatosensory system is the body sensation. It monitors a wide variety of stimuli from all over the body from the activity in receptors found in the skin, and proprioceptors in the muscle and the joints The functions of the Somatosensory system - to monitor the contract of objects and surface with the skin, particularly the hands and feet - to report the position of body segments in space and in relation to each other(body scheme) - to initiate sensory activity for the interpretation of harmful stimuli The Somatic Sensory Cortex - Primary somatosensory cortex(SⅠ) : Brodmann's areas 1,2,3a and 3b - Seconcary somatosensory cortex(SⅡ) >20 types of receptors in skin: touc h, temperature, stretch, etc 2 pathways to brain Dorsal columns Precise touch, joint angle, etc. Crosses side at medulla Antero-lateral Tract Coarse information regarding pain and temperature Convergence of information Crosses side at entry in spinal colu mn Hierarchy of Sensory Fibers Specialized Receptors Single Nerve Fiber Sensory Fiber Bundle Spinal Nerve Dorsal Root Ganglia Dorsal Column Nuclei Spinal Motorneurons or Reticular Formation Thalamus Primary and Association Cortex (Parietal Lobe) Organization Each tract mediates specific modalities of sensation, somatotopic organization in tracts and cortex Mechanoreceptive Thermoreceptive Mechanical displacement of nerve endings Touch (fine and diffuse), pressure, vibration, kinesthesia Cold and Heat Nociceptive Pain Specialized Receptors Receptors specialize by type of stimulus Adaptiveness: Reduction of response to sustained stimuli Basic Types of Sensory Receptors Encapsulated Endings Free Nerve Endings (pain, temp, some tactile) Adapting (tactile) Pacinian corpuscle: deep pressure touch and high frequency vibration. Meissner’s corpuscle: light touch, such as the fingertips, palms, soles, lips, tongue, face Nonadapting Expanded Tip Endings (tactile, temp) Moderately adapting ◆ Primary Afferent Axons (Fibers) 1) Classified according to their diameters 2) The greater their diameter, the greater their conduction velocities 3) Peripheral nerve fibers show differences in the following functional properties Three neuron Organization 1st Order 2nd Order Dorsal Root Ganglion Enter CNS at spinal cord or brainstem Project to opposite side crossing midline to thalamus 3rd Order Thalamus neurons which project to cortex Anatomical Divisions Dorsal Column-Medial Lemniscal (or Epicritic System) Fine discriminative touch, vibration, limb position, kinesthesia & deep pressure Position sense Proprioception - Awareness of limb position Kinesthesia - Awareness of limb movement Anterolateral (or Protopathic System) Pain, temperature and diffuse touch Lateral spinothalamic tract Anterior spinothalamic tract Dorsal Column-Medial Lemniscal System Important for skilled movements Stereognosis - Fine touch discrimination Graphesthesia - Recognizing numbers written on body Two and multiple point touch Deep touch Receptors Meissner’s and Pacinian Corpuscles Encapsulated end receptors Highly sensitive and adaptable Muscle Spindle Organs Kinesthesia Proprioception Neural Pathways Neural Pathways Fasciculus Gracilis Fasciculus Cuneatus Path Mediate discriminative Touch from different Body areas; follow three-neuron organization Spinal Ganglion (1) Gracilis or Cuneatus Nucleus (2) Through Medial Lemniscus to Thalamus (3) Thalamus to Cortex Levels of Reception Fasciculus Gracilis Sacral to Midthoracic Level Lower Body Fasciculus Cuneatus Above Midthoracic Level Upper Body Pathway Spinal Cord Brainstem Nuclei Thalamus (N. Ventral Posterolateralis) Thalamus through Internal Capsule to Primary Sensory Parietal Cortex Primary to Association Cortex Mapped spatially (homunculus) Medial Lemniscal Pathway: Mechanoreceptors & Proprioception The homunculus Anterolateral system Pain, Temperature, & Diffuse Touch Three-tier neuron organization system 1. 2. 3. Enter at spinal ganglion (1st) Cross in spinal tract (2nd order) Ventral posterolateral n. of thalamus (3rd) Two Tracts Lateral Spinothalamic Anterospinothalamic Pain and Temperature Anterolateral System Cerebral Cortex 3 Thalmus 2 1 Brainstem/spinal cord Spino-Thalamic Pathway: Temperature & Pain Lateral Spinothalamic Tract Receptors - Free Nerve Endings Neural Pathway Nocioceptors (pain) Dorsolateral spinal cord (up or down several segments) spinal cord entrance Substantial Gelatinosa and Proprius Where 1st order neurons connect with 2nd order neurons Lateral Spinothalamic Tract Cross Midline (2nd order) Spinal Lemniscus (brainstem) Thalamus (VPL) to Cortex Collaterals to Subcortical structures Anterospinothalamic Tract Discrimination of Diffuse touch Receptors: All three types Neural Pathway Encapsulated endings Free nerve endings Expanded tip endings Skin to ganglia (1st) Dorsolateral spinal cord (up and down seg) Proprius and Substantia Gelatinosa (2nd) Go to spinothalamic tract to VPL (thalamus) to postcentral gyrus Collaterals to subcortical structures Clinically, interruption causes no obvious deficit Unconscious Proprioception Conscious proprioception by dorsal columnmedial lemniscal system Unconscious involved in walking, articulating, writing, swallowing, and eye movement. Two order neural system Tracts Dorsal Spinocerebellar Cuneocerebellar Ventral Spinocerebellar Receptors Muscle spindles and Golgi tendon organs located in muscles and limb joints Ventral Spinocerebellar Tract Mediates unconscious proprioception Lower limbs to bilateral cerebellum Sacral and Lumbar levels through ventrolateral Spinocerebellar tract to opposite cerebellar hemisphere Dorsal Spinocerebellar Tract Mediates unconscious proprioception Lower limbs and middle regions of body to to bilateral cerebellum Spinal ganglion to nucleus dorsalis of Clark at third lumbar segment Do not cross and enter ipsilateral cerebellar hemisphere Cuneocerebellar Tract Mediates upper limbs and neck Uncrossed fibers to ipsilateral external cuneate nucleus to cerebellum Clinical Considerations Romberg used to determine some function Difficult to test clinically Sensory abnormalities Cerebral cortex region - conscious proprioception two-point discrimination stereognosis touch & pain Cerebellum region - ataxia Prerequisites of Treatment Normalising muscle tone Suitable working positions Stimulationg sensating without increasing spasticity Cooperation of patient Allowing sufficient time Consideration of other disabilities Repetition of stimuli Variation of stimuli Adjustment of training intensity Haptics