* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1 - Schoolwires.net
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
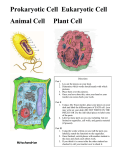
Cells Review Questions Name ______________ Briefly Answer The Following. 1. Why do cells’ nuclei have pores on the outside? Nuclear pores allow mRNA to leave the nucleus and travel to the ribosome. 2. Name the cell part that modifies and packages proteins. Golgi Apparatus 3. What is the function of the mitochondria? The mitochondria generates energy for the cell in the form of ATP 4. What is the function of the rough endoplasmic reticulum? The RER makes proteins (because it has ribosomes on it) and transports proteins throughout the cell 5. What are groups of tissues called? Organ 6. What is the function of the lysosomes in the cell? They can help break down glucose and can also kill the cell if needed 7. Name one organelle that is found in the plant cell, but not in the animal cell. Cell wall & Choloroplasts 8. What is one type of cell that has a flagellum? (Guys…you should know this!) Sperm Cell 9. What part of the microscope should not be used when looking at specimens under high power? Coarse adjustment knob 10. What is the large organelle in the plants cell that stores water? Vacuole 11. What organelle produces proteins? Ribosomes 12. What is the gel-like material in the cell that contains the organelles? Cytoplasm 13. What was the first type of cells seen through a microscope? Cork Cells 14. Why is it advantageous for cells to be small? High surface-tovolume ratio allows molecules to travel swiftly in and out of the cell. 15. Define Prokaryotic. Bacterial cell with no membrane bound organelles or nucleus 16. Give two examples of eukaryotic cells. Plant cell; Human cell 17. Explain the difference between the outside of the plant and animal cell. Both plant and animal cells have cell membranes. Plant cells have an extra layer of protection in the form of a cell wall. 18. What part of the cell do molecules have to pass to get inside? Cell membrane 19. Describe the major component of the plasma membrane. Phospholipids are the largest component of the cell membrane. They are made of polar phosphate heads and 2 lipid tails 20. Which organelle controls the activities inside the cell? Nucleus