* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Protein Folding File
Phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Folding@home wikipedia , lookup
Protein design wikipedia , lookup
Homology modeling wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Protein (nutrient) wikipedia , lookup
Intrinsically disordered proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein domain wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Protein folding wikipedia , lookup
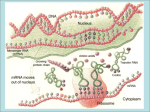
Protein Folding http://www.wiley.com/college/boyer/0470003790/animations/protein_folding/protein_folding.htm 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. In your own words, what are proteins? Proteins are considered a polymer. Why? What are the two main structural motifs present in secondary folding of amino acid chains? What type of bonding stabilizes alpha helices and beta sheets? In addition to H-bonding, what type of bonding leads to stronger covalent bonds between amino acids? After secondary structures are formed, what is the primary driving force for tertiary folding? A protein may not always fold ‘correctly’. What do scientists call the folded secondary configuration that does not result in a functioning protein? After a productive conformation is found the protein will fold into tertiary conformation. What type of structure is it called when two protein subunits interact to make the final functional protein? Do proteins always fold properly? How does the cell ensure that proteins are folded properly? Does this process require energy? Protein Folding http://www.wiley.com/college/boyer/0470003790/animations/protein_folding/protein_folding.htm 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. In your own words, what are proteins? Proteins are considered a polymer. Why? What are the two main structural motifs present in secondary folding of amino acid chains? What type of bonding stabilizes alpha helices and beta sheets? In addition to H-bonding, what type of bonding leads to stronger covalent bonds between amino acids? After secondary structures are formed, what is the primary driving force for tertiary folding? A protein may not always fold ‘correctly’. What do scientists call the folded secondary configuration that does not result in a functioning protein? After a productive conformation is found the protein will fold into tertiary conformation. What type of structure is it called when two protein subunits interact to make the final functional protein? Do proteins always fold properly? How does the cell ensure that proteins are folded properly? Does this process require energy?