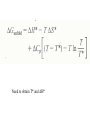* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical cascade wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Expression vector wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Ancestral sequence reconstruction wikipedia , lookup
Paracrine signalling wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Bimolecular fluorescence complementation wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Interactome wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Protein purification wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
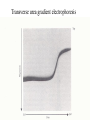
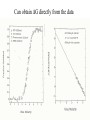
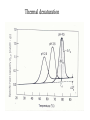
Protein folding reading: Creighton sections 7.1, 7.3, 7.4 and 7.5 The nature of the unfolded state Not completely random. Molten globule state: Creighton pg 292 Denaturants: Urea Guanidinium Chloride Temperature pH Other solvents Most common chemical denaturants used in protein folding studies Effects of additives to protein solutions Effects of some organic solvents Increase solubility of polar and nonpolar side chains Effects of the counter anion Absorbance Aromatic amino acid residues absorb strongly Folding transitions Transverse urea gradient electrophoresis Can obtain DG directly from the data Thermal denaturation Need to obtain T* and DH* DG for different proteins Cooperative versus noncooperative folding Simulated Sequential mechanism: U -> I1 -> I2 -> N Linked functions The folding pathway for BPTI