* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Organelles
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
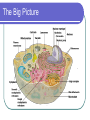
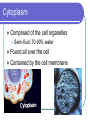
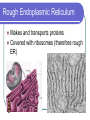
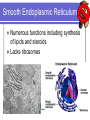
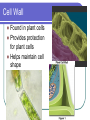
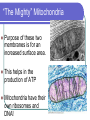
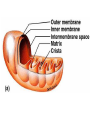
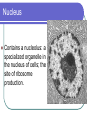
Eukaryotic Cell Organelles Structure & Function It’s a small, small, world… The Big Picture All Different Shapes and Sizes! Eukaryotic cells are everywhere! Cytoplasm Comprised of the cell organelles Semi-fluid: 70-90% water Found all over the cell Contained by the cell membrane Ribosomes Site of protein synthesis Can either be free in cytoplasm or attached to rough endoplasmic reticulum Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Makes and transports proteins Covered with ribosomes (therefore rough ER) Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Numerous functions including synthesis of lipids and steroids Lacks ribosomes Golgi Apparatus Consists of closely layered stacks of membranes Modifies, stores, and ships products of the Endoplasmic reticulum (proteins) Lysosome Digestive organelle in eukaryotic cells Defend a cell from invading bacteria and viruses and break down damaged or worn out cell parts Centrioles Found in animal cells Involved in cell division Composed of microtubules Used to pull chromosomes apart Central Vacuole A fluid filled sac used for storage of materials needed by the cell Helps with cellular digestion In plant cells the vacuole usually stores water and ions that are needed in the cell Cell Wall Found in plant cells Provides protection for plant cells Helps maintain cell shape “The Colorful” Chloroplast Found in plant cells (not animal) Allows plants to produce food through the process of photosynthesis “The Colorful” Chloroplast Contains the pigment chlorophyll This is what gives plants their green color Contains a double membrane “The Mighty” Mitochondria Supply ENERGY to the cell They are bean shaped and have two membranes “The Mighty” Mitochondria Purpose of these two membranes is for an increased surface area. This helps in the production of ATP Mitochondria have their own ribosomes and DNA! Cell Membrane Cells of all organisms are surrounded by a cell membrane. It is a thin layer of lipid and protein that separates the cells contents from its environment Cell Membrane Function: Controls what enters and exits the cell (the gatekeeper) Nucleus Contains most of the cell’s genetic material Control center for the cell Surrounded by a double membrane called an nuclear envelope Nucleus Contains a nucleolus: a specialized organelle in the nucleus of cells; the site of ribosome production. Cytoskeleton Fibers that provide structural support for the cell Helps the cell move