* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download cell structure and function research projects
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
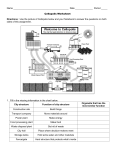
Cell Structure and Function HS-LS-1: Systems of specialized cells within organisms help them perform the essential functions of life. Summarize the structures and functions of organelles found in a eukaryotic cell (including nucleus, mitochondria, chloroplasts, lysosomes, vacuoles, ribososmes, endoplasmic reticulum [ER], Golgi apparatus, cilia, flagella, cell membrane, nuclear membrane, cell wall, cytoplasm). Performance objectives: 1. Students will be reminded and be expected to know the content of the cell theory 2. Students will understand the difference between plant and animal cells and which organelles are present in which type of cell. 3. Students will create a memorable way to think of each organelle in the analogy activity. 4. Students will learn the organelles of the cell, what their role is within the cell, and how they function within the cell. Students will express their knowledge by a paired research project. 5. Students will be able to explain how the different organelles in the cell are connected. Students will do this by applying information gathered in the research activity to the Journey into the Cell activity. Concept Exploration: 1. Analogies and organelles- individual activity You will be given an organelle. On a piece of paper, you will create a comparison between your organelle and something in everyday life (they have the same function). Draw the organelle and the item being compared. Explain the analogy on your paper. Share the analogy with the class. 2. Research activity- pair exercise You will be paired with another student(s) with the same organelles as you and together you will research your organelle. Use creditable sources for information. -.edu, .gov, reference books, text book, etc. Focus research on answering the following questions: o Year discovered o o o o o Country of discovery Scientist who discovered your organelle Number present in cells Relative size in the cell What kind of cell the organelle is found in: Prokaryote, Eukaryote, plant, animal, bacteria, fungi o Role (function) o Disorder information… o Number of disorders known o Name of one disorder, its symptoms and life expectancy o One interesting fact Research for each organelle will be compiled and made available as reference material for the next activity 3. Concept application Each team will assemble and edit scientific information on cells, then write a creative story. The team will decide which kind of cell they want to work with (plant or animal). Organelles and sections will be assigned to individual team members. The team will use the organizer sheet and planning page to help create the story. Journey into a Cell: Planning Page Worksheet to be completed as a team Members of this team: ______________, ______________, ________________, ________________ In this activity your team will assemble and edit scientific information on cells, then write a creative story. 1. Decide what type of cell to write about within your group. (plant or animal) record on organizer sheet 2. Assign a section of the story to each member of your group. Sections are listed below 3. Discuss and outline your story (intro, body, conclusion) with your team. Remember to use the same character names and tenses in each section. 4. Begin researching and writing your story. Some materials you may want or choose to use are: Encyclopedia, text book, notes, research activity, Internet. (Remember the acceptable places to gather information from the Internet.) Record individual research on the organizer sheet. 5. After gathering information your team will come together to complete the planning page. The planning page will help you prepare to write and illustrate a creative story. Completing the worksheets will ensure a quality story. Use the planning page to create an outline and the organizer sheet to help you add facts to your story. (Don’t forget to cite your source.) Title of Story: _________________________________________________________________ Each team member is responsible for WRITING about and ILLUSTRATING the 3 organelles listed under their SECTION. The organelles do not necessarily have to be discussed in that section. For example, your team may wish to discuss ribosomes, ER, and chloroplasts in sections 2 and/or 3. P=plant cell organelle A= animal cell organelle Written By: Section 1 (introduction) Describe the setting of your story. How did you get into the cell? What kind of cell are you in? What do you see around you? Written By: P: cell wall, cell membrane, cytoplasm A: lysosomes, cell membrane, cytoplasm P/A:nucleus, chromosomes, nucleolus Written by: Section 3 Continue the adventure. How are you traveling around the cell? How are you reacting to what is happening inside the cell? How are the different cell parts reacting with you? Written by: Section 4 (Conclusion) Resolve the adventure. How will your story end? How will you leave the cell (if you do)? “Wrap up your story” P: ribosomes, ER (rough and smooth), chloroplasts A: ribosomes, ER (rough and smooth), centrioles P/A: mitochondria, vacuole, Golgi bodies Section 2 What is happening to you? Begin to develop the plot. What is it like to be inside of a cell? What is the focus of this story? Will you be trying to get out of the cell, or will something happen to you? Journey into a cell: Organizer sheet Name: _______________________ Date: ________________________ Use this page to help you organize what you know about an animal or plant cell. Be specific when recording your facts. You can elaborate on them when writing your story. (Each team member is responsible for 3-4 cell organelles and/or parts) What parts/organelles are you responsible for? Where are they located What do these cell parts/organelles look like? Facts about_________ (type of cell A or P) And __________,_________, __________ organelles. What are the functions of each cell part? How does each of the cell parts/organelles work with other parts of the cell? Review and Evaluation Each student will be evaluated throughout the lesson plan. They will be evaluated on their understanding of the organelles in the analogy activity, their ability to conduct an information search and the relevance of information gathered during their search. Students will be evaluated on their ability to apply gathered knowledge and their understanding of the structure and function of cells in the story activity. o This activity provides individual and team grades. Students will be graded individually on correctness of the information on the organelles they were responsible for and on the section of cell interaction they were responsible for. Students will be graded as a team for the content, flow, correctness, and relevance of their story.